 [Image: Screen grab from Sir John Soane’s Museum].
[Image: Screen grab from Sir John Soane’s Museum].
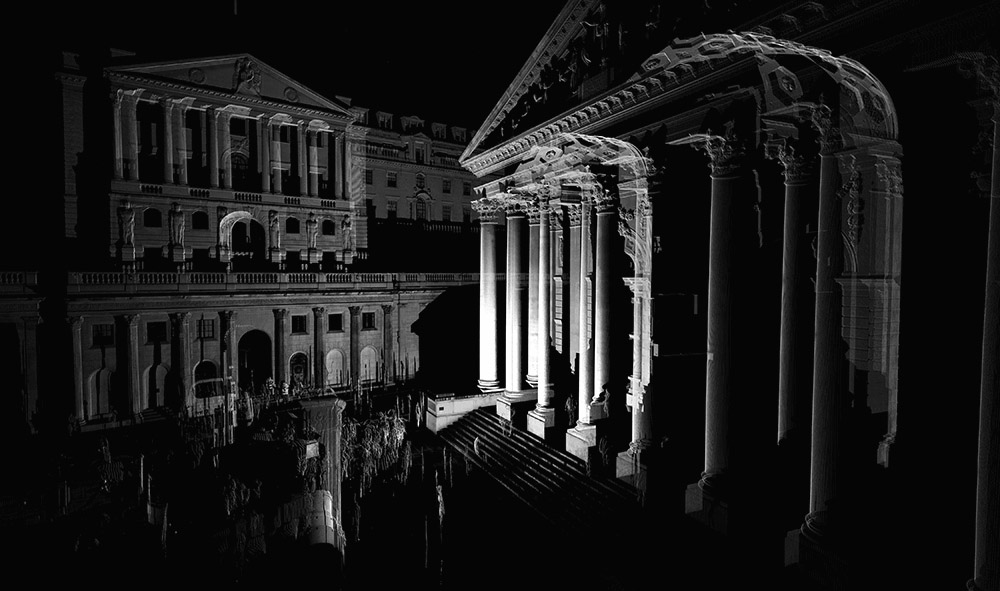
One of my favorite museums, Sir John Soane’s Museum in London, has teamed up with ScanLAB Projects for a new, 3D introduction to the Soane’s collections.
 [Image: Screen grab from Sir John Soane’s Museum].
[Image: Screen grab from Sir John Soane’s Museum].
“We are using the latest in 3D technology,” the Museum explains, “to scan and digitize a wide selection of Museum rooms and objects—including Soane’s Model Room, and the ancient Egyptian sarcophagus of King Seti I.”
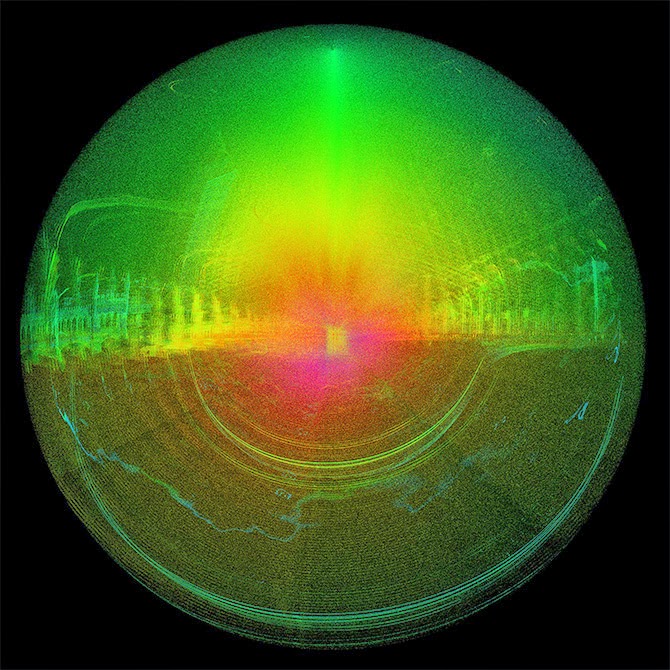
The opening animations alone—pulling viewers straight into the facade of the building, like a submarine passing impossibly through a luminous reef—are well worth the click.
 [Image: Screen grab from Sir John Soane’s Museum].
[Image: Screen grab from Sir John Soane’s Museum].
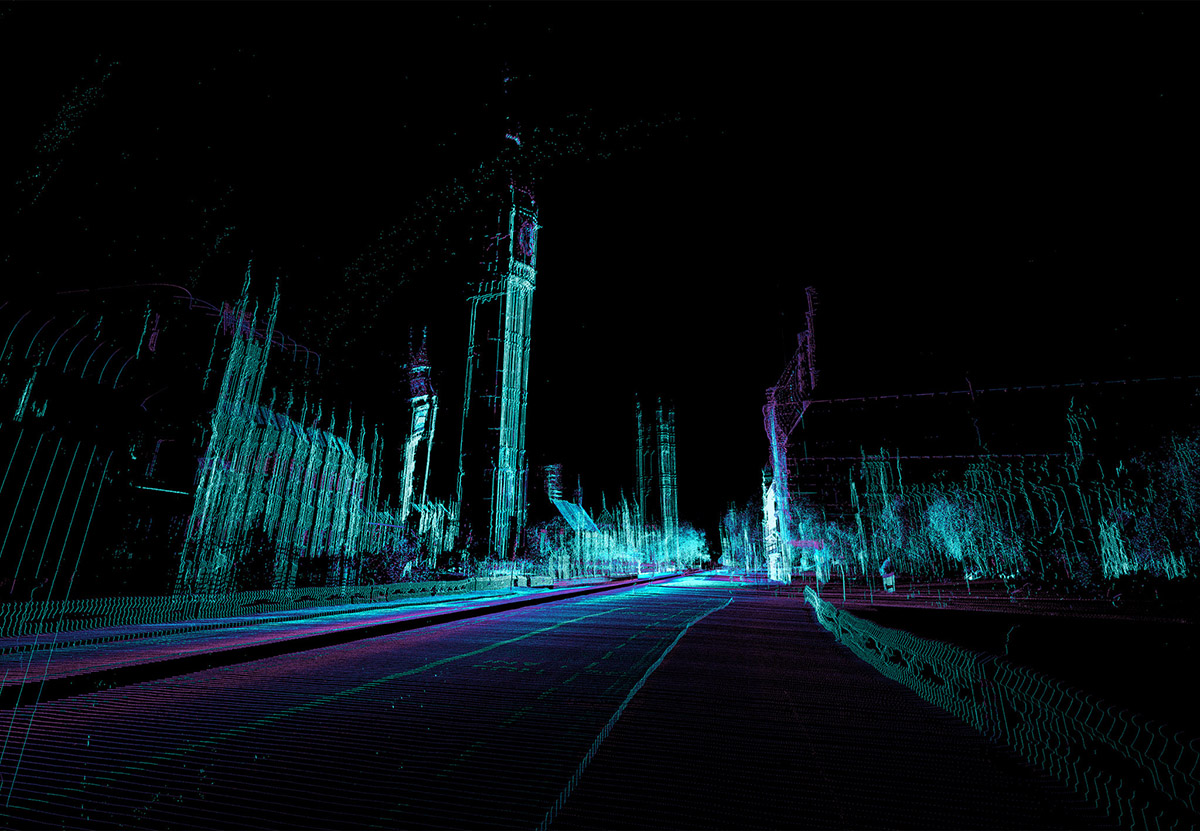
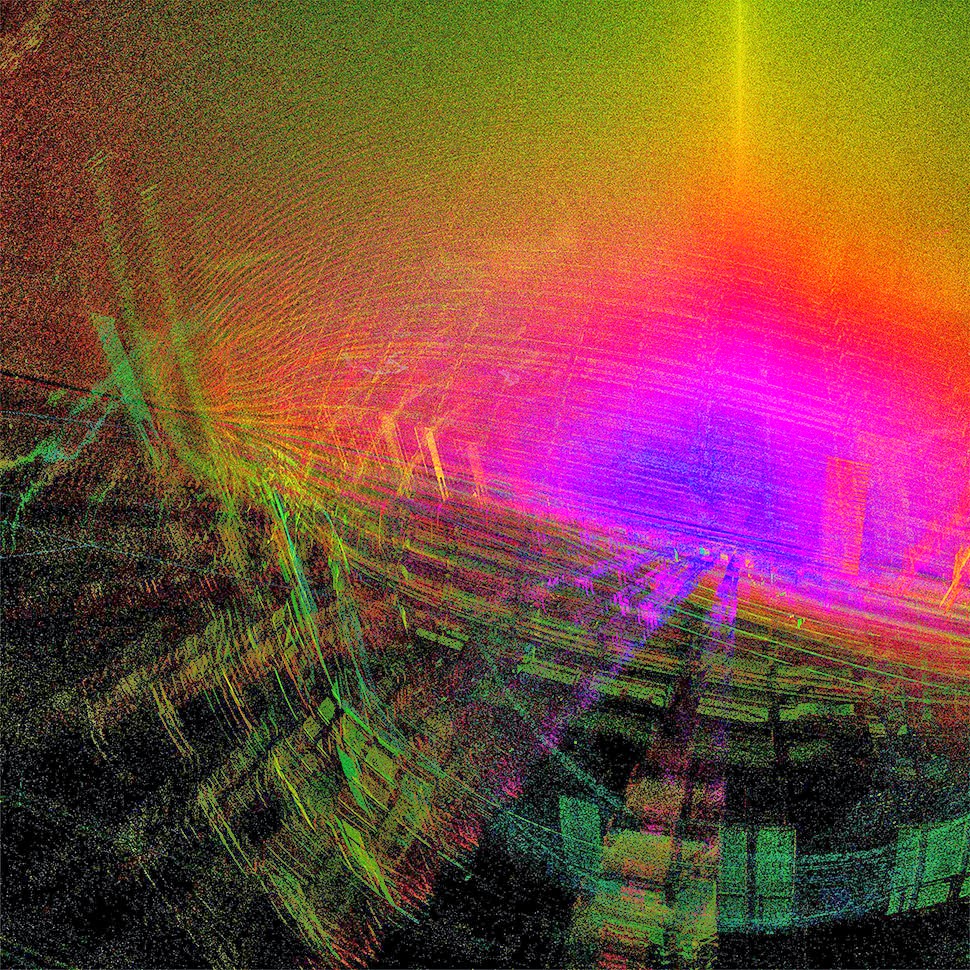
The museum’s interior walls become translucent screens through which the rest of Soane’s home is visible. Rooms shimmer beneath other rooms, with even deeper chambers visible behind them, golden, hive-like, lit from within. Like a camera built to capture only where things overlap.
In fact, I could watch entire, feature-length films shot this way: cutting through walls, dissecting cities, forming a great narrative clockwork of action ticking away in shining blocks of space. As if the future of cinema is already here, it’s just hidden—for now—in the guise of avant-garde architectural representation.
 [Image: Screen grab from Sir John Soane’s Museum].
[Image: Screen grab from Sir John Soane’s Museum].
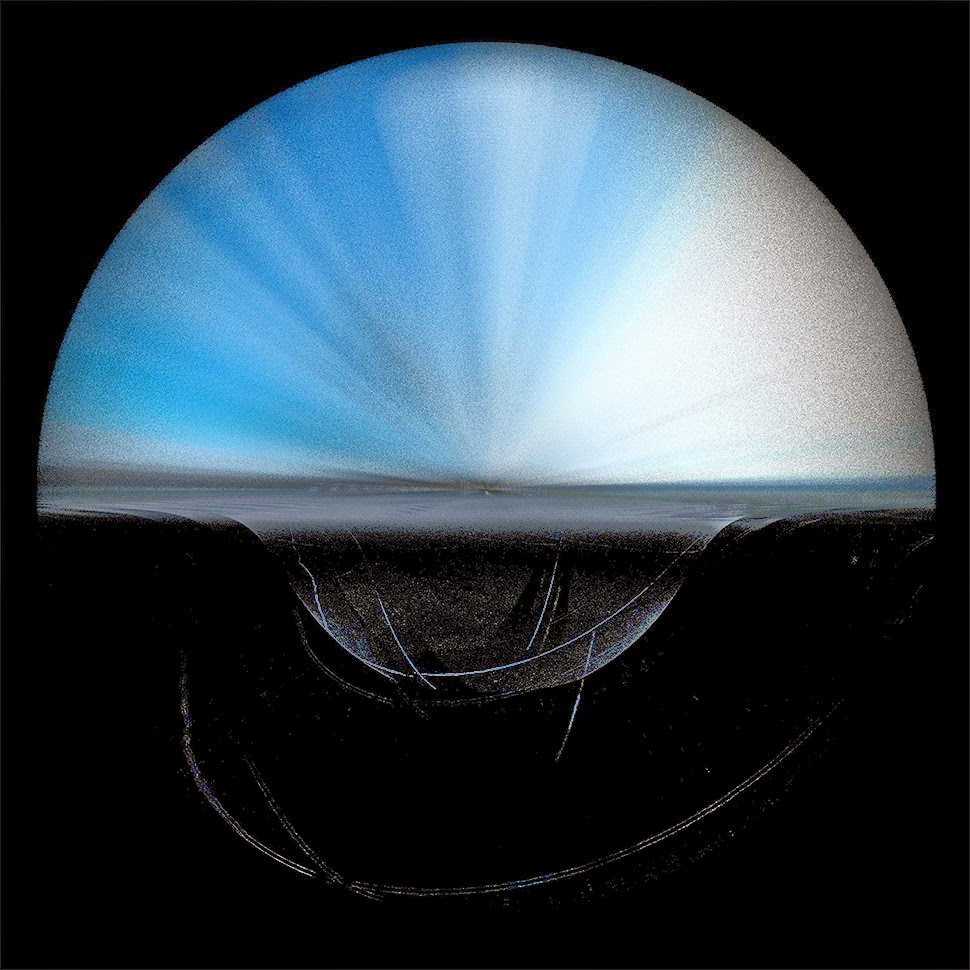
ScanLAB’s work—such as in Rome, beneath the streets of London, or in strange new forms of portraiture—continues to have the remarkable effect of revealing every architectural space as actually existing in a state more like a cobweb.
Hallways become bridges crossing the black vacuum of space; individual rooms and galleries become unreal fogs of ornament and detail, hanging in a context of nothing.
It thus seems a perfect fit for a place as bewildering and over-stuffed as the Soane Museum, that coiling maze of archaeological artifacts and art historical cross-references, connected to itself through narrow stairways and convex mirrors.
Of course, this also begs the question of how architecture could be redesigned for maximizing the effects of this particular mode of visualization. What materials, what sequences, what placements of doors and walls would lend itself particularly well to 3-dimensional laser scanning?
The new site also includes high-res, downloadable images of the artifacts themselves—

 [Images: The sarcophagus of King Seti I; courtesy Sir John Soane’s Museum].
[Images: The sarcophagus of King Seti I; courtesy Sir John Soane’s Museum].
—including Seti I’s sarcophagus, as seen above.
Click through to the Soane Museum for more.
(Elsewhere: The Dream Life of Driverless Cars).

 [Image by
[Image by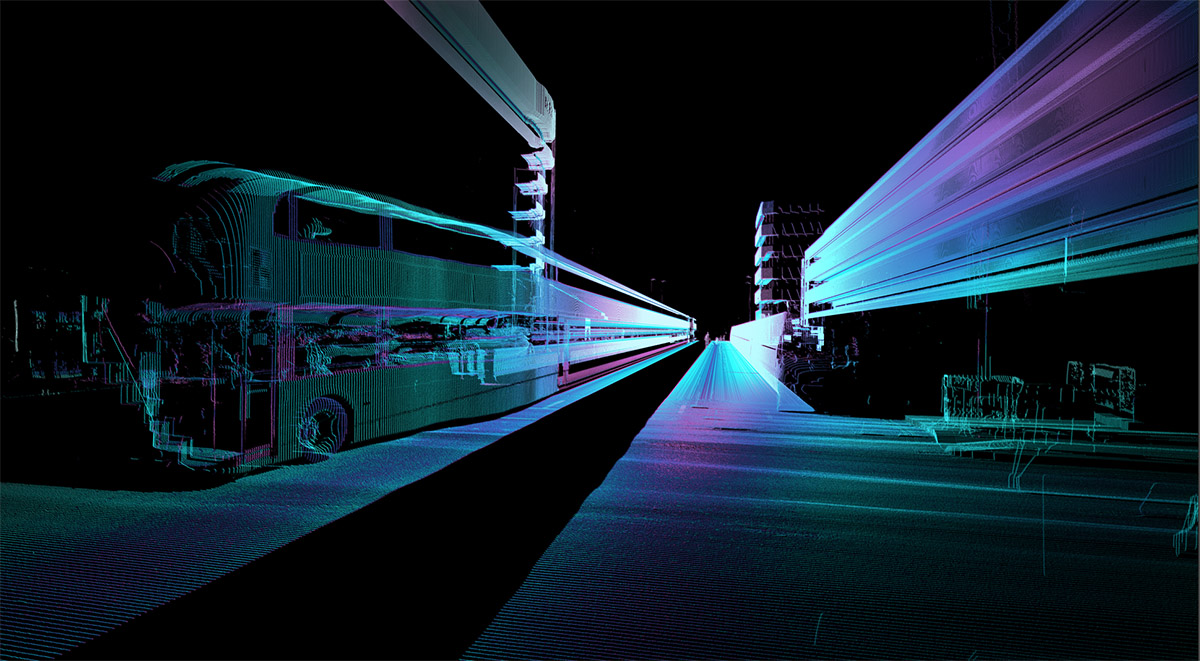  [Image by
[Image by 
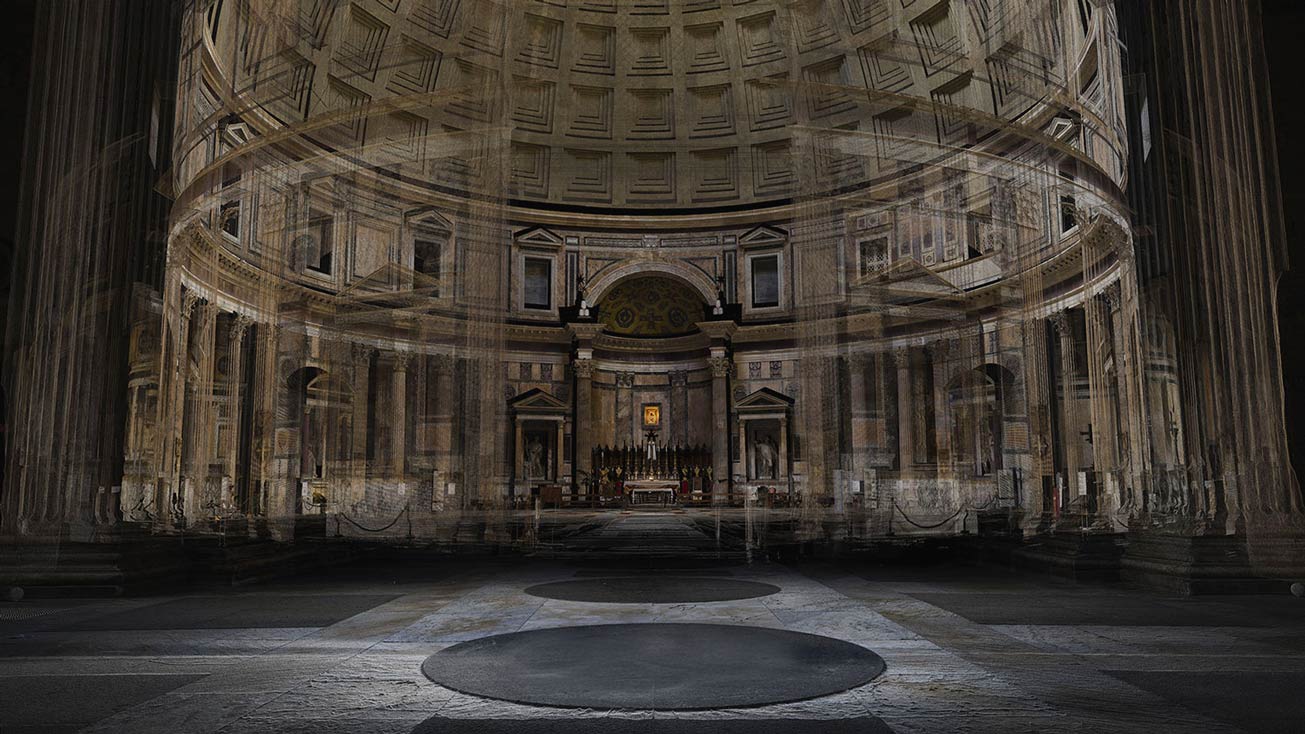 [Image: A laser scan of the Pantheon, courtesy
[Image: A laser scan of the Pantheon, courtesy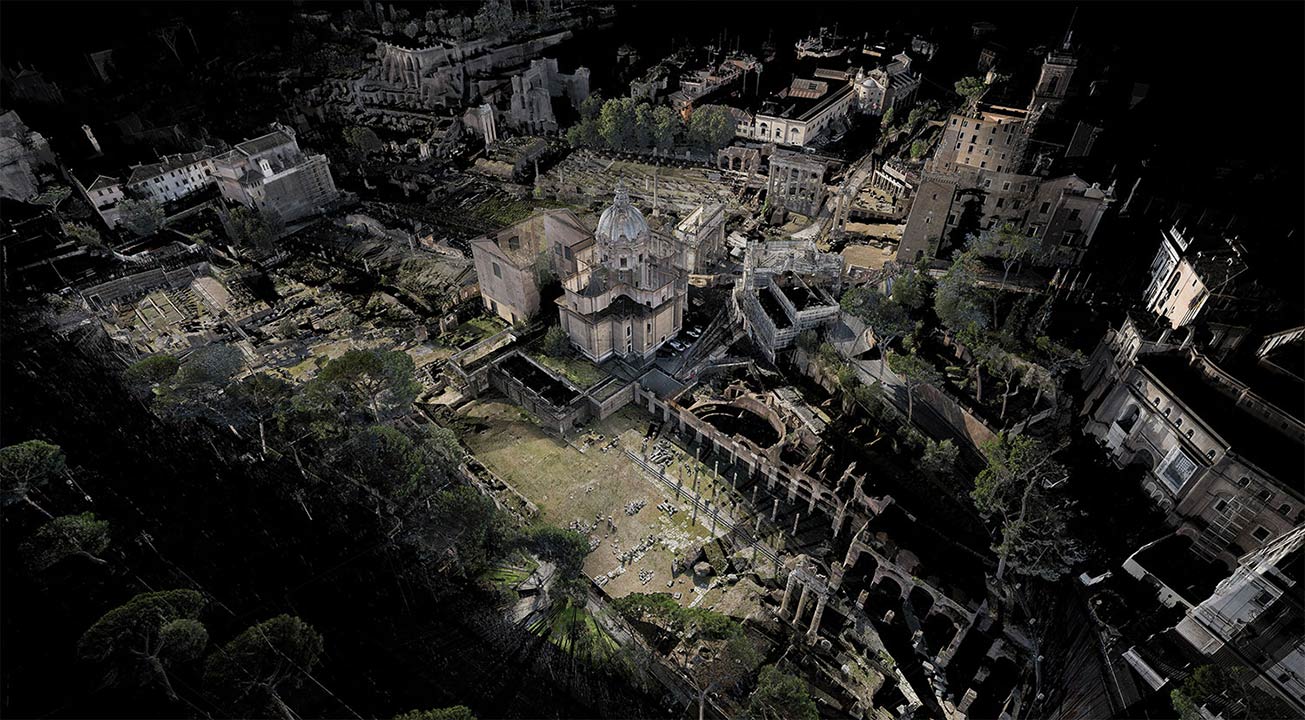  [Image: Courtesy
[Image: Courtesy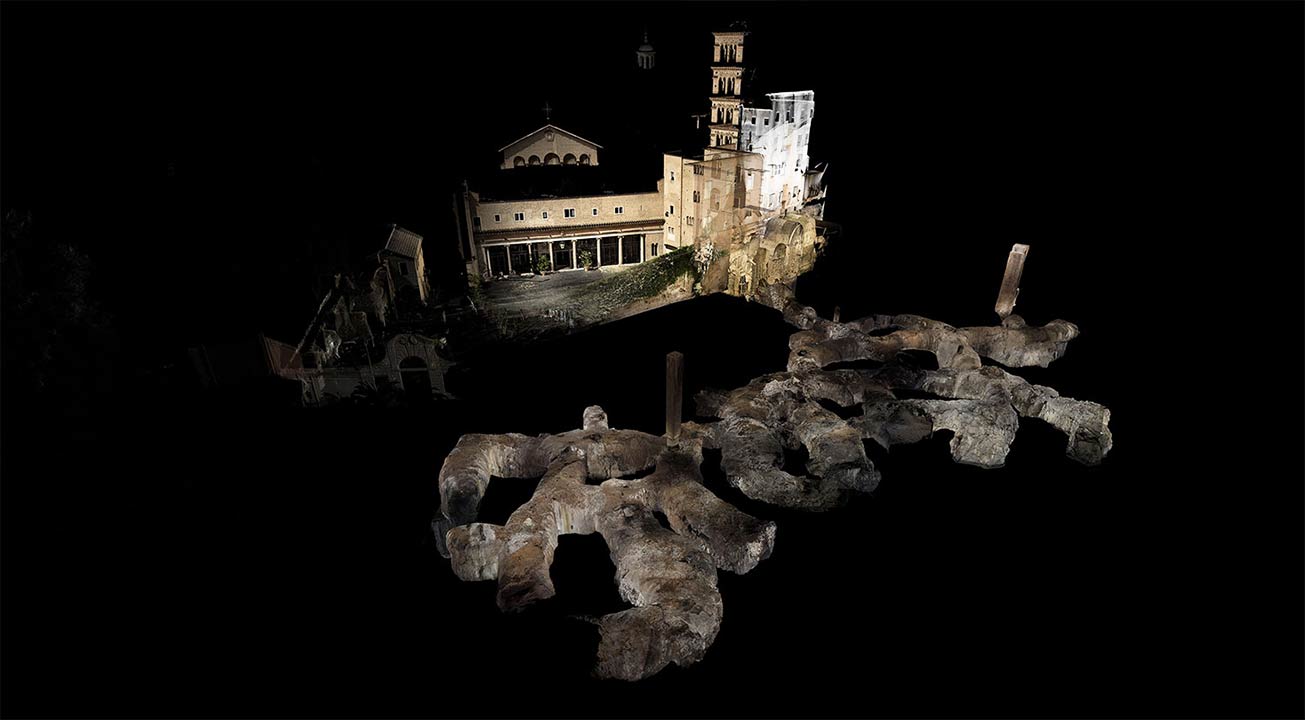  [Image: Courtesy
[Image: Courtesy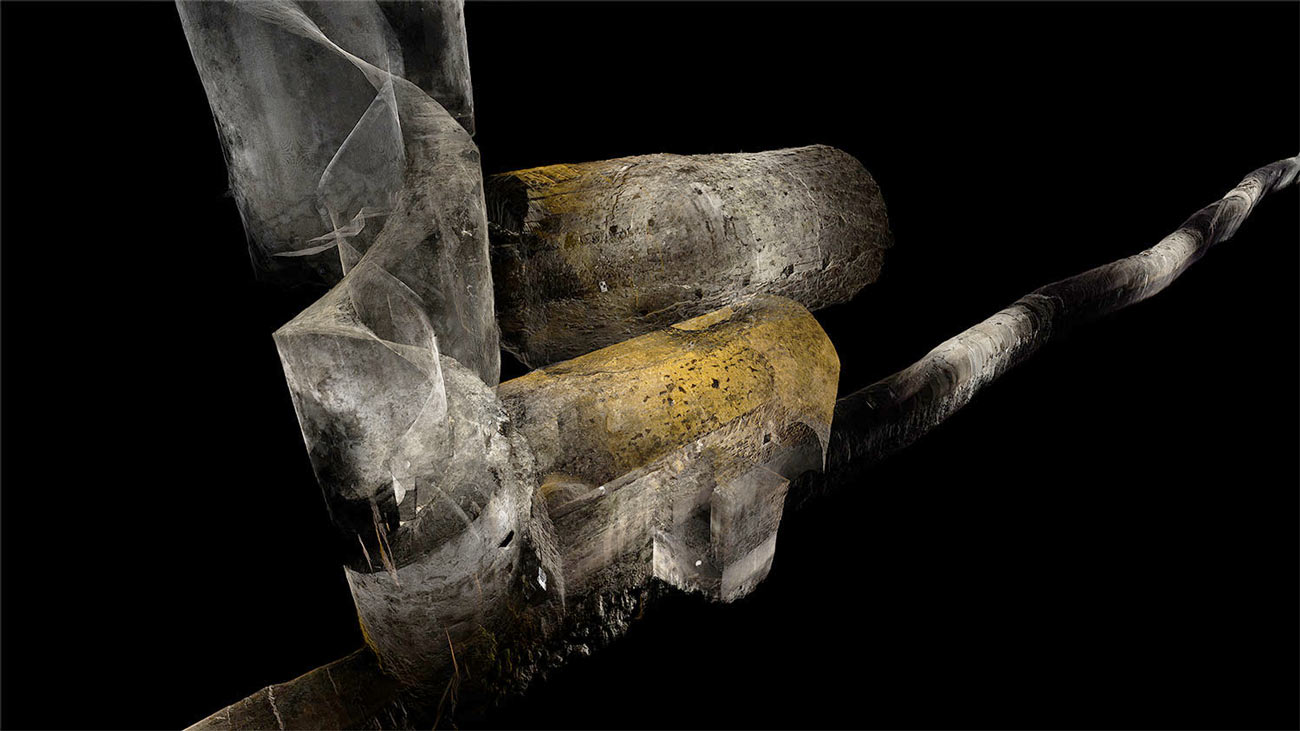  [Image: Courtesy
[Image: Courtesy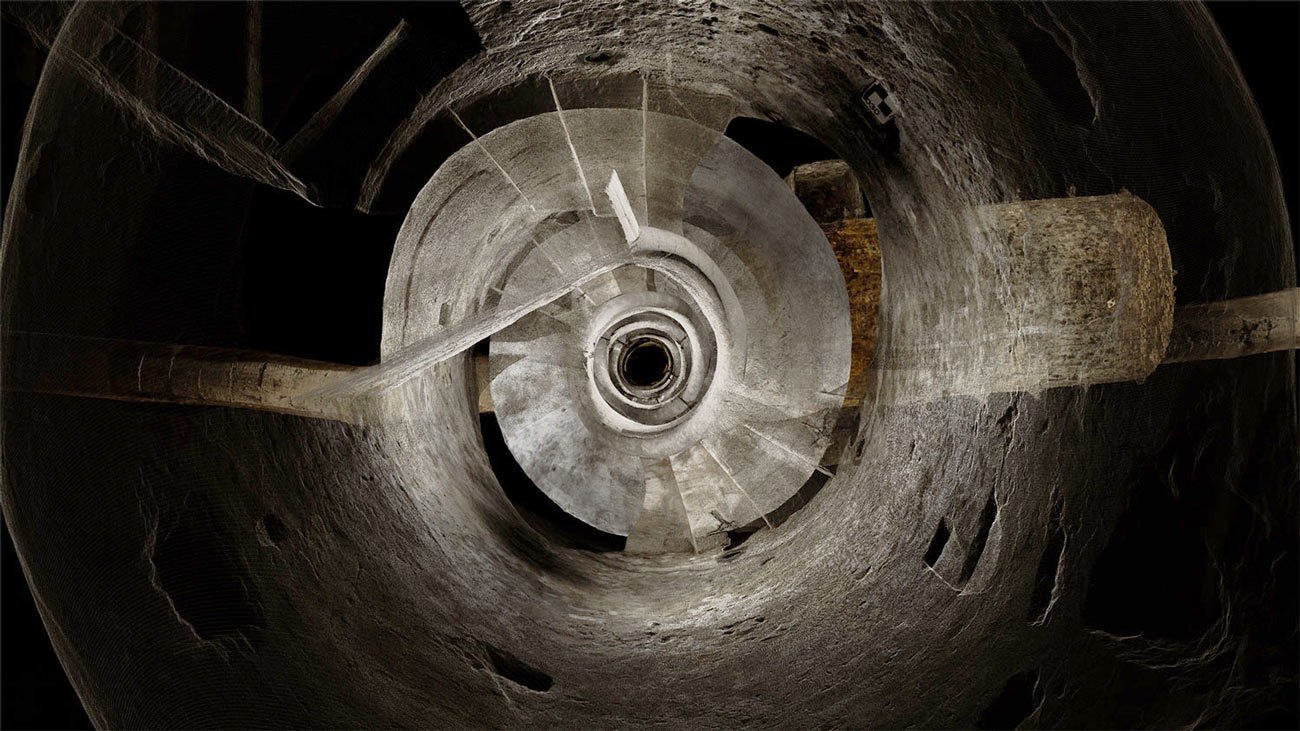  [Image: Courtesy
[Image: Courtesy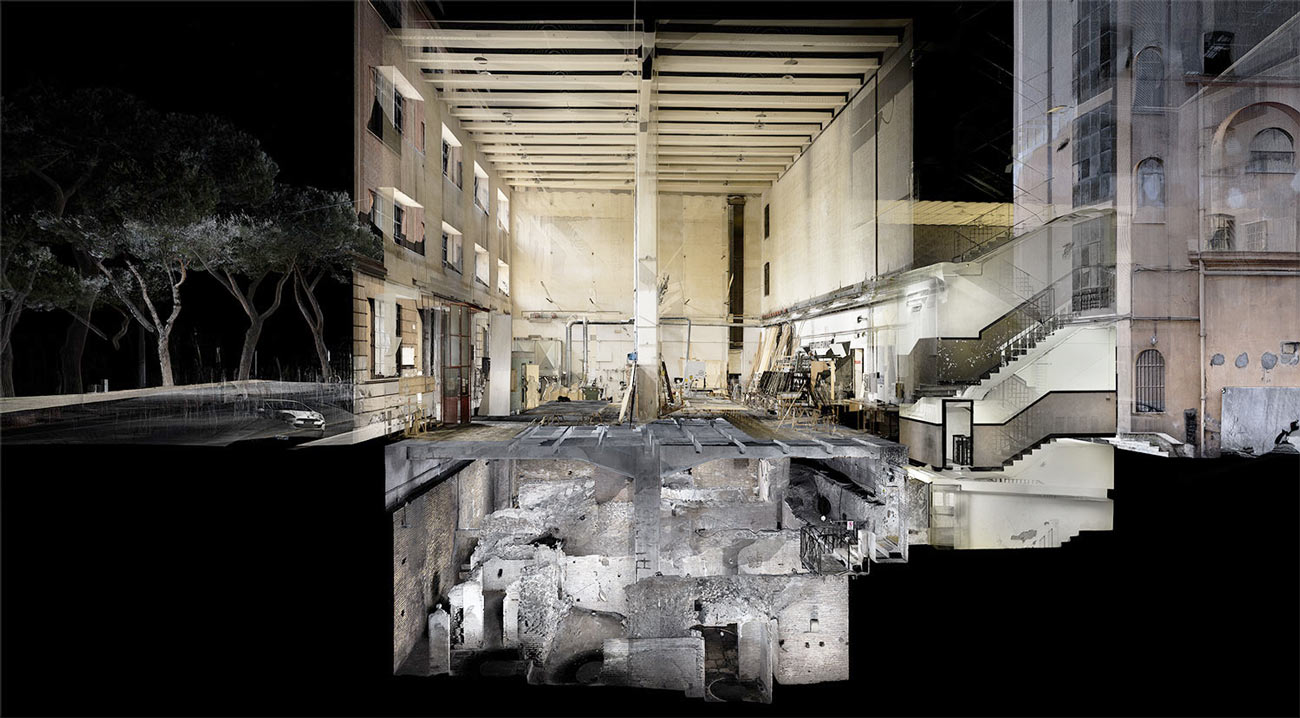  [Image: In the ruined basements of architectural simultaneity;
[Image: In the ruined basements of architectural simultaneity; 
 [Image: By
[Image: By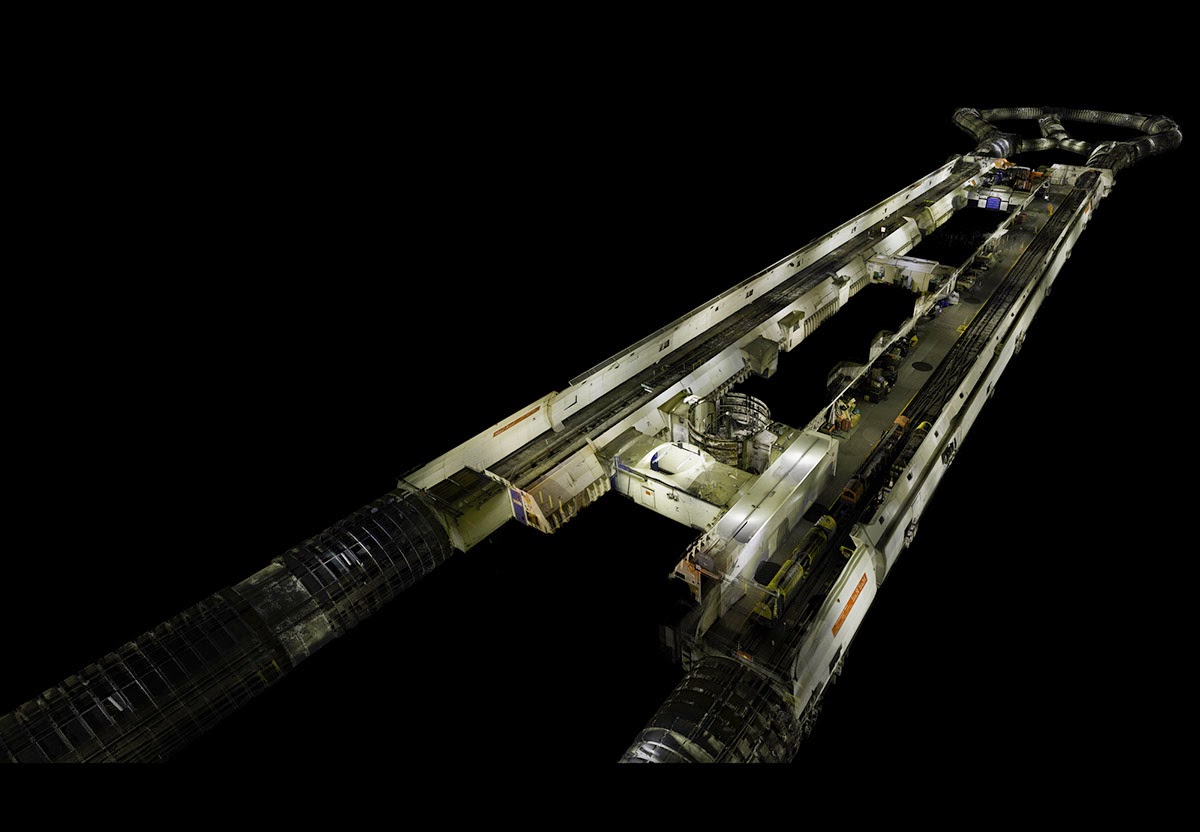  [Image: By
[Image: By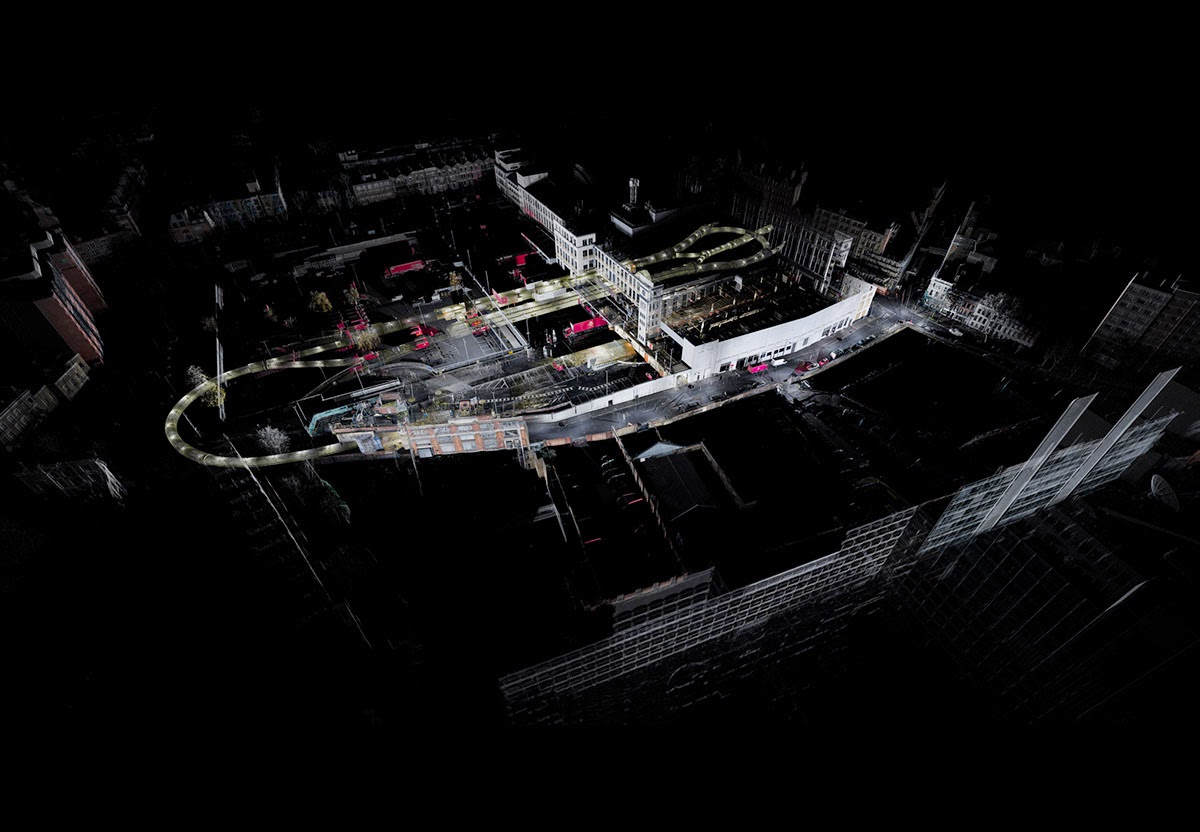  [Image: By
[Image: By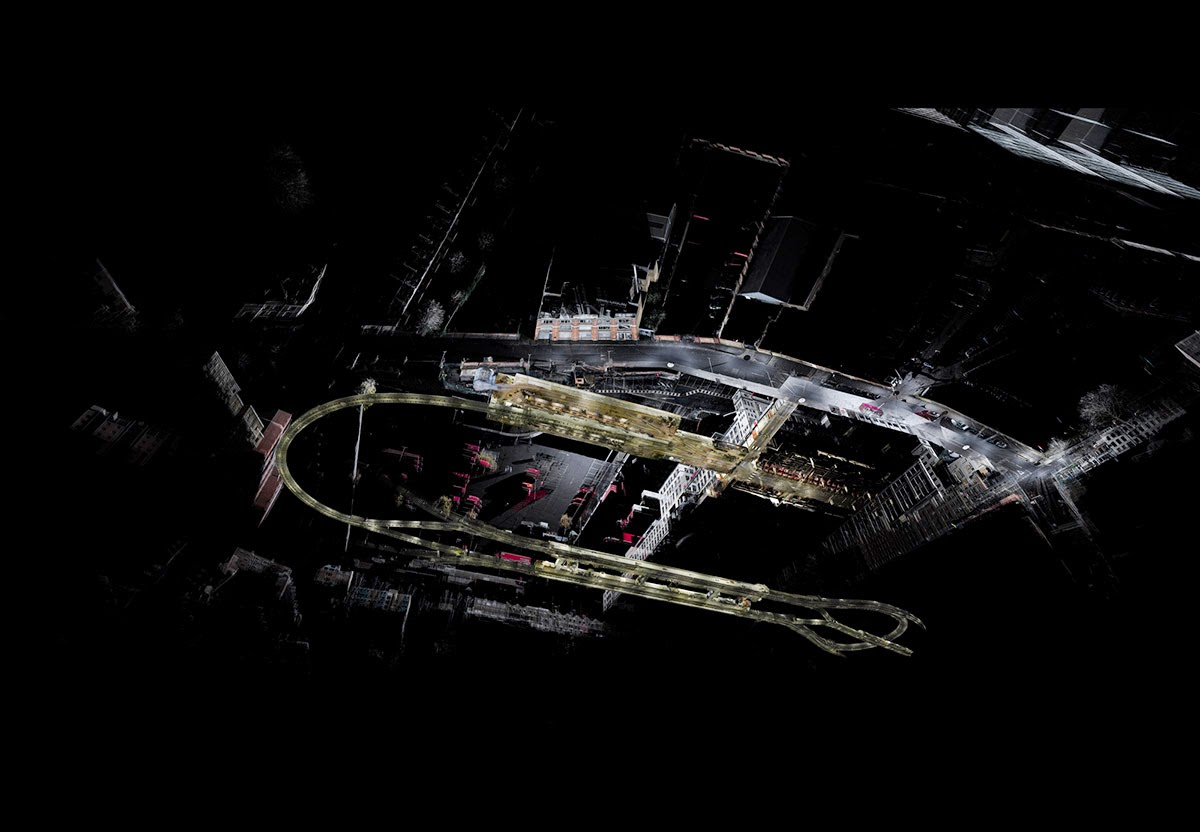  [Image: By
[Image: By  [Image: By
[Image: By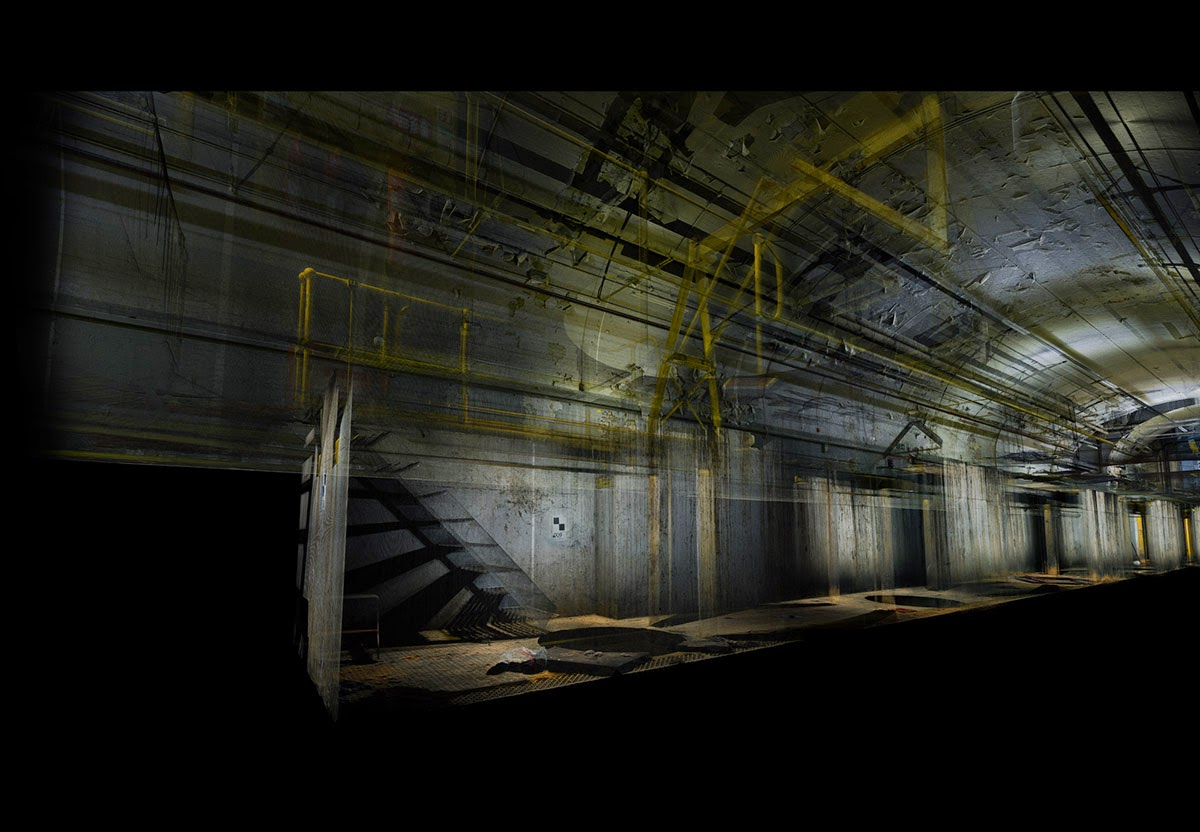  [Image: By
[Image: By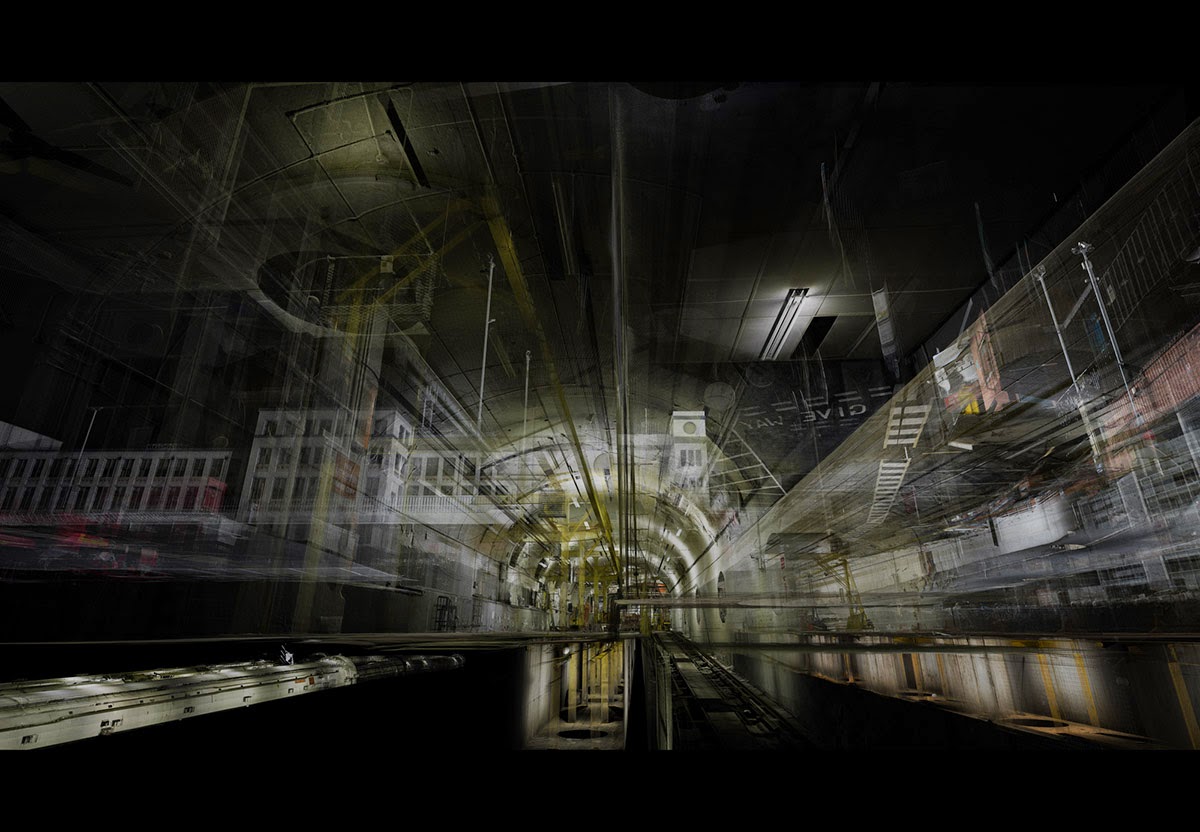  [Image: By
[Image: By 
 [Image:
[Image: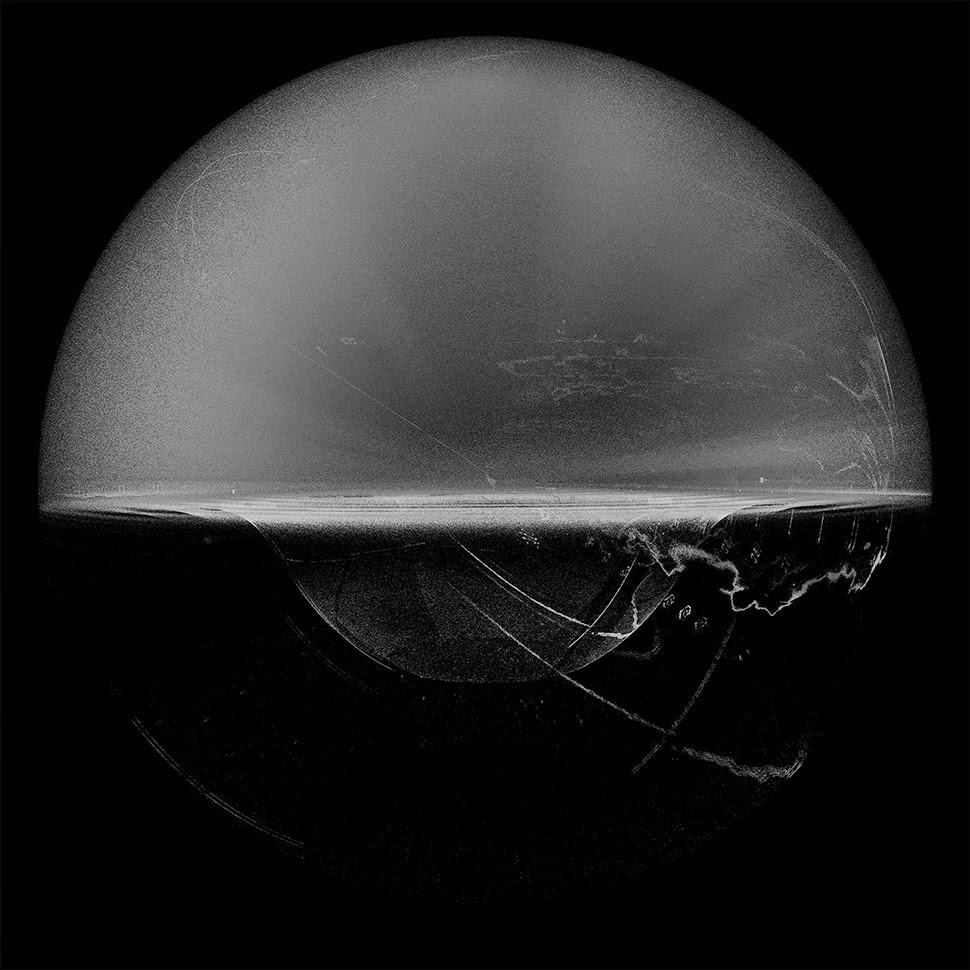  [Image:
[Image: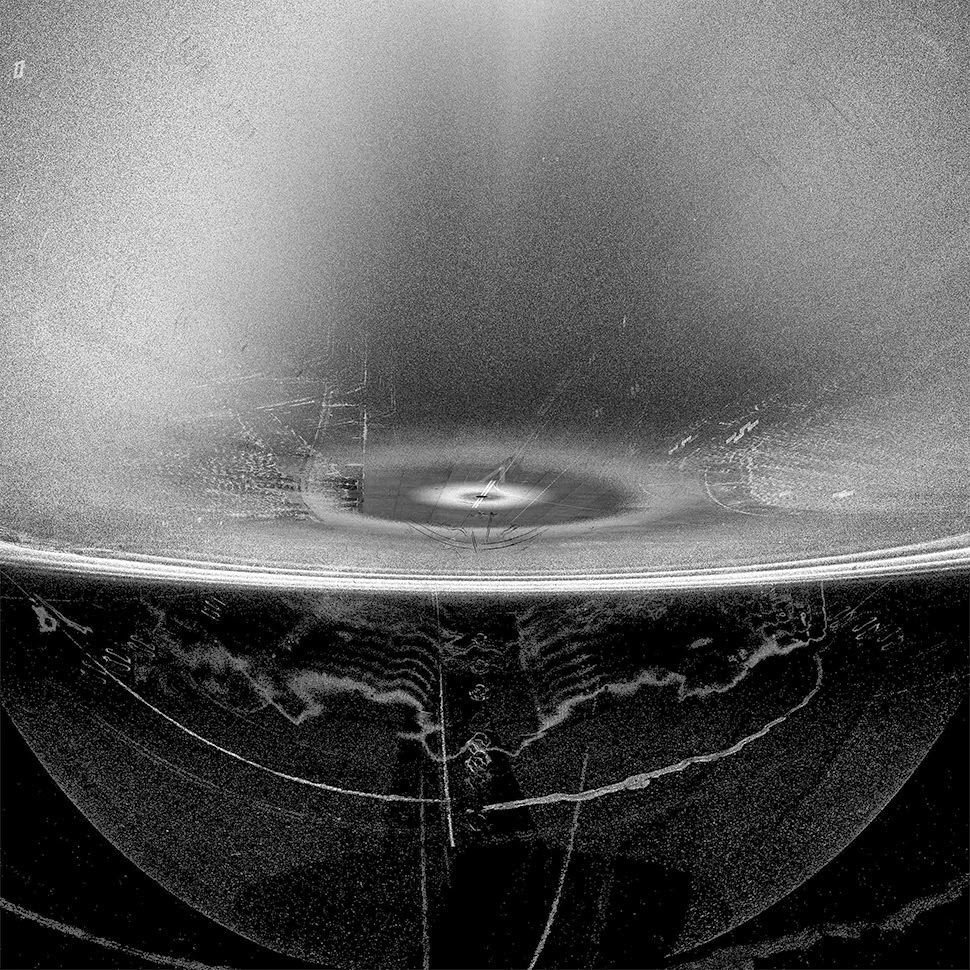  [Image:
[Image: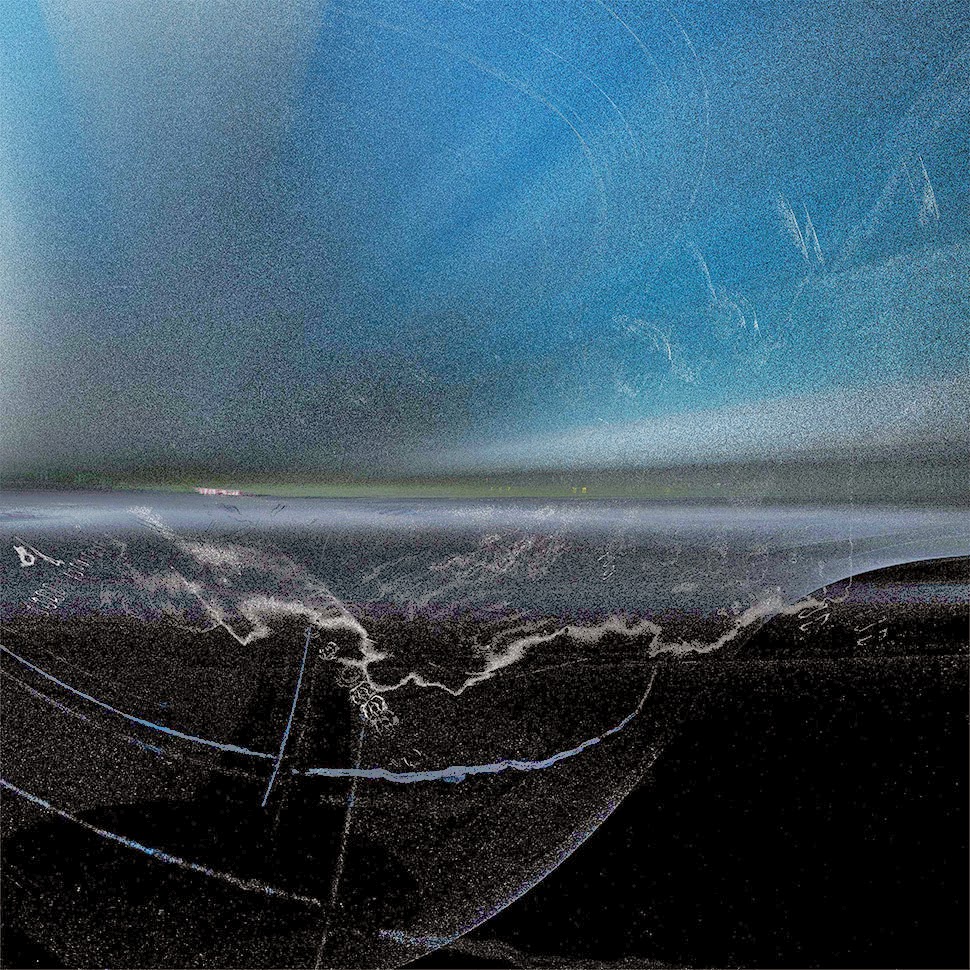  [Image:
[Image: 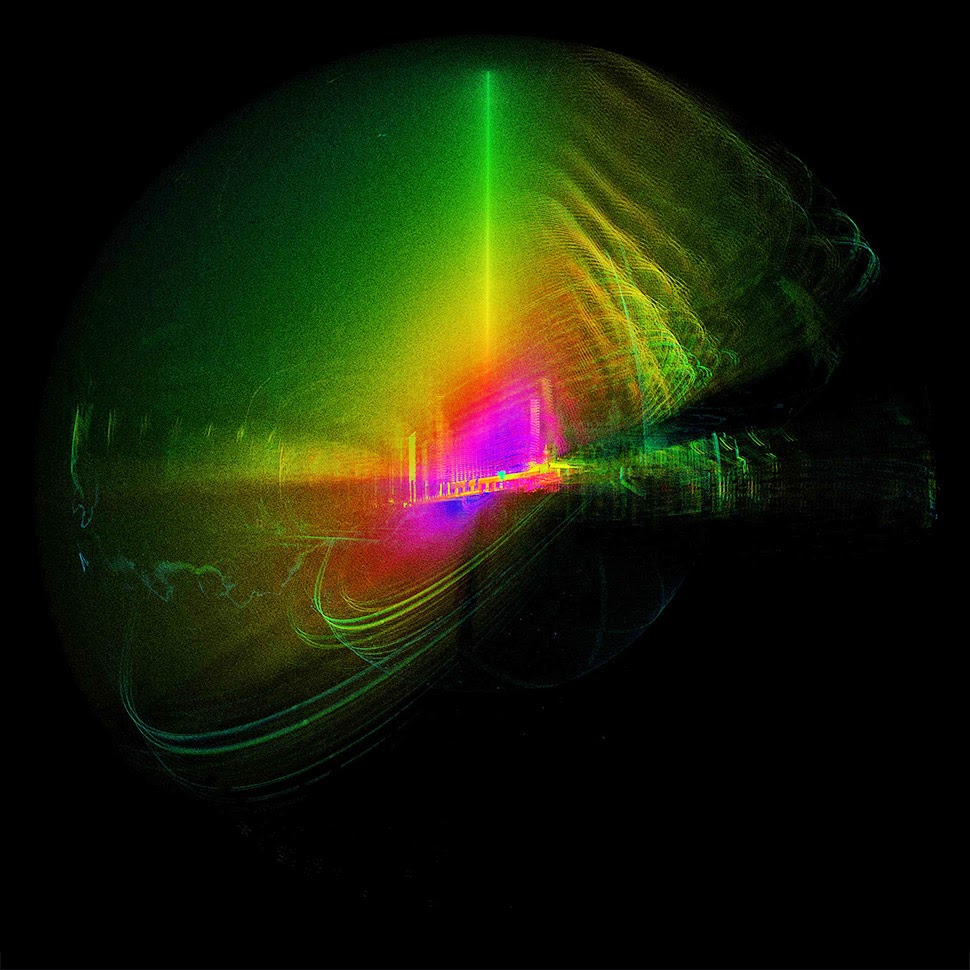
 [Images:
[Images: 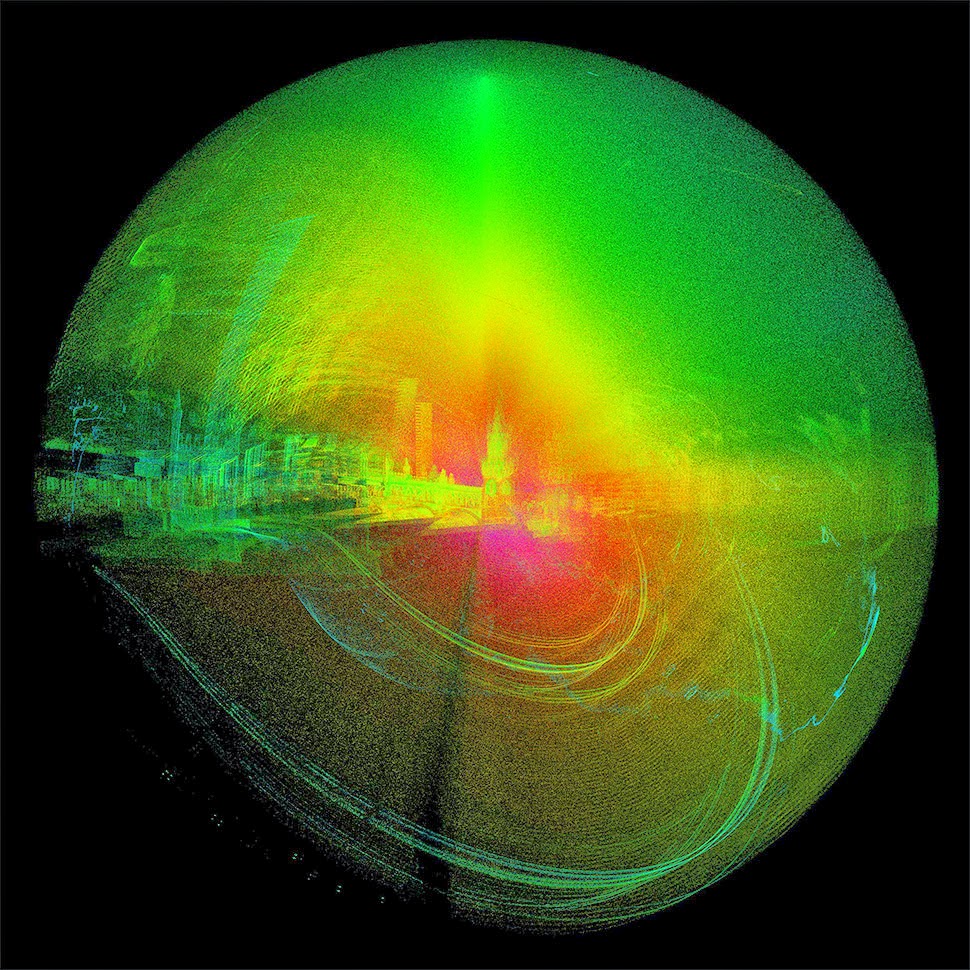
 [Images:
[Images: 
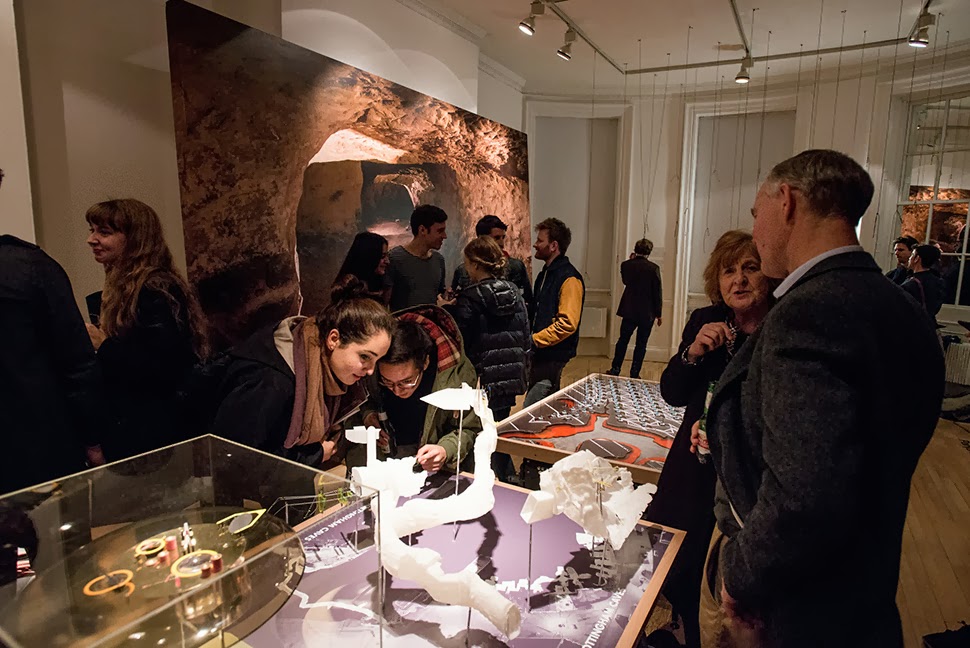
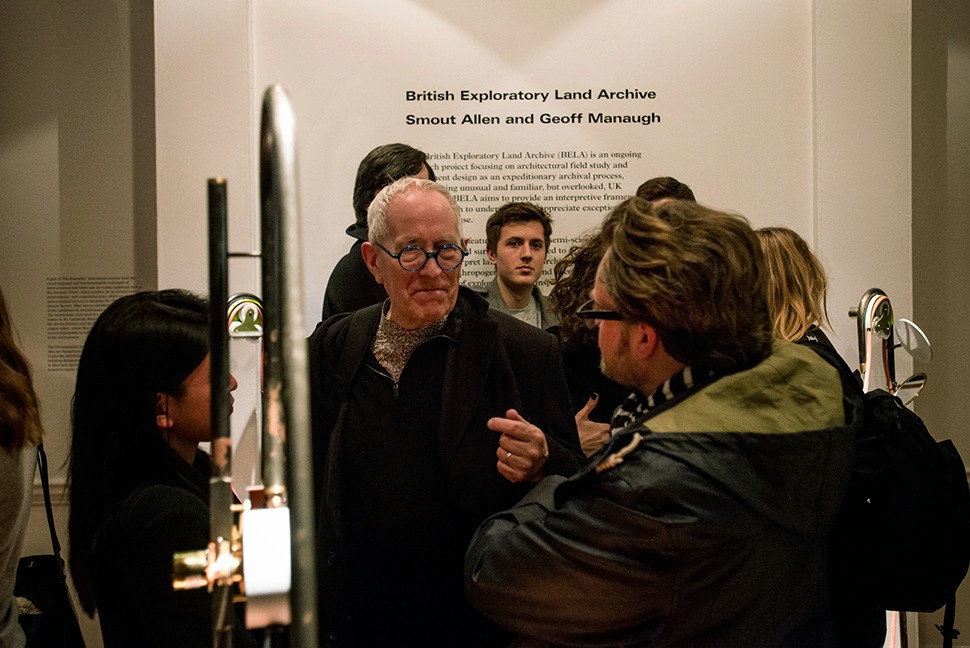
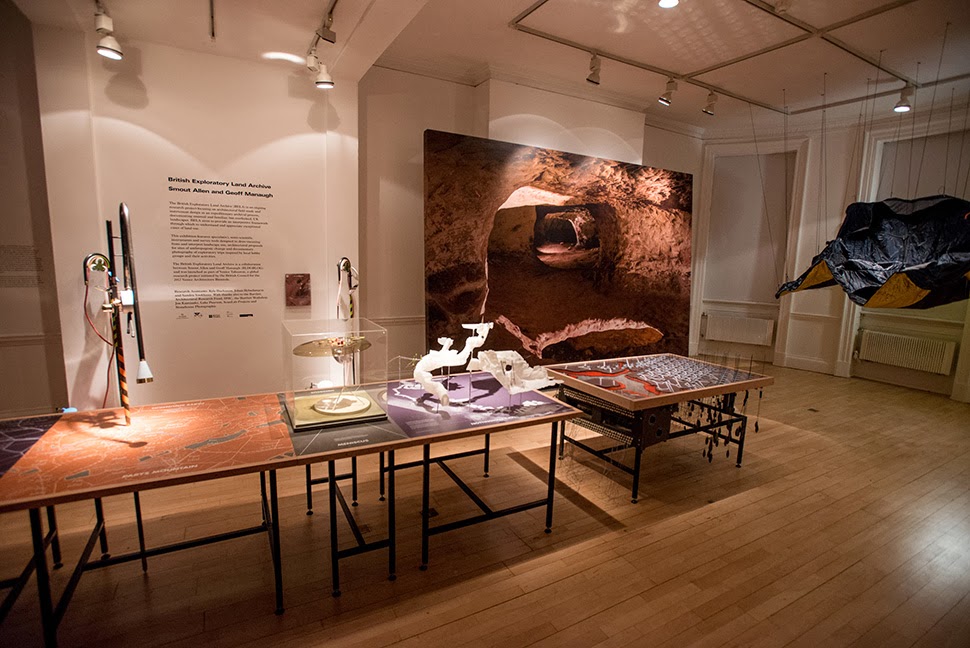 Last week, over at the
Last week, over at the  Although I was unfortunately not able to be in London to attend the opening party, I was absolutely over the moon to get all these photographs, taken by
Although I was unfortunately not able to be in London to attend the opening party, I was absolutely over the moon to get all these photographs, taken by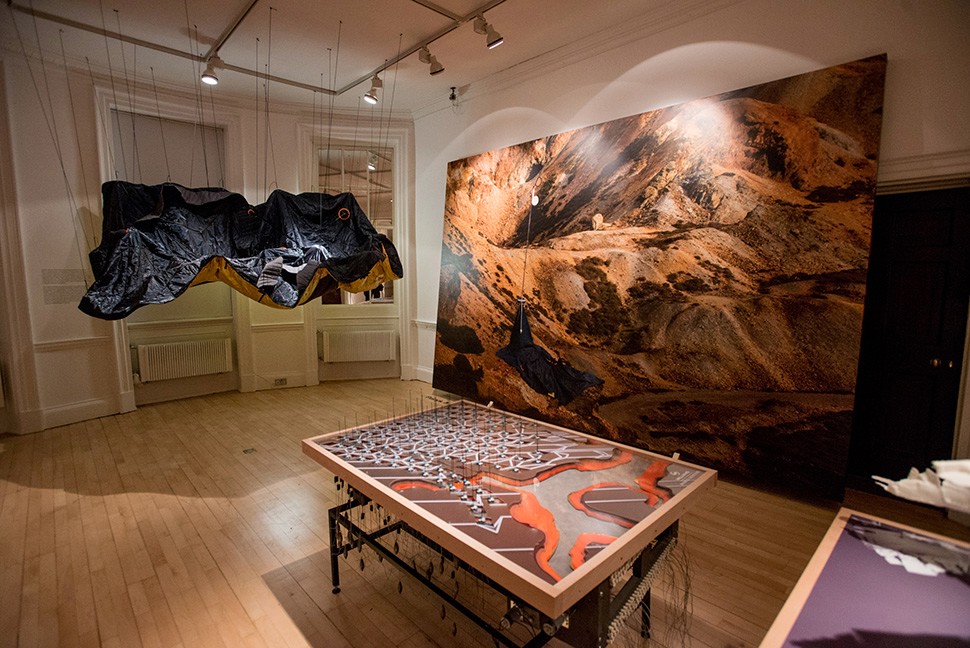 
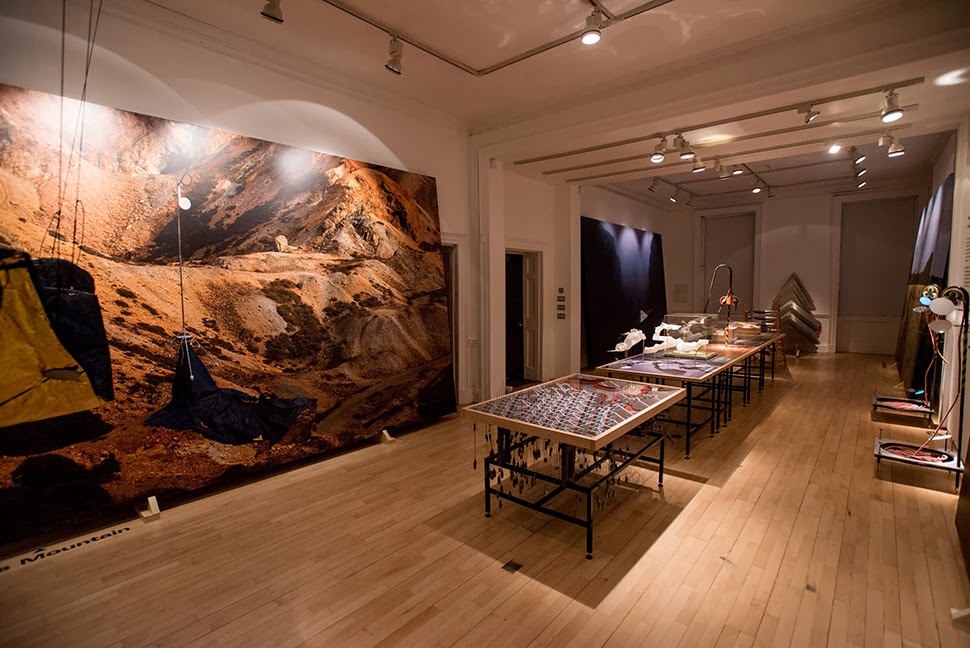
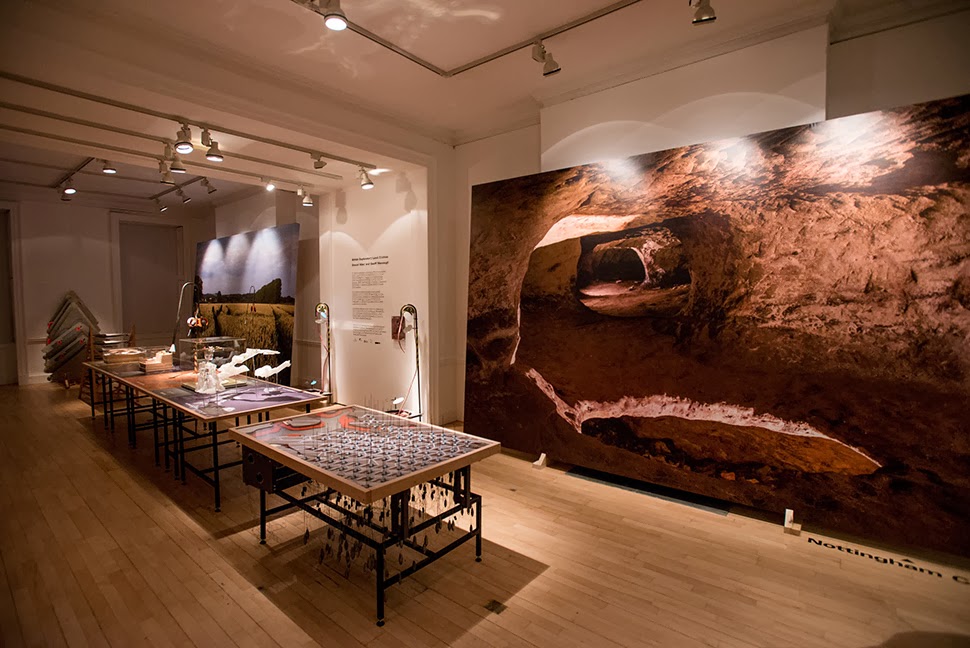
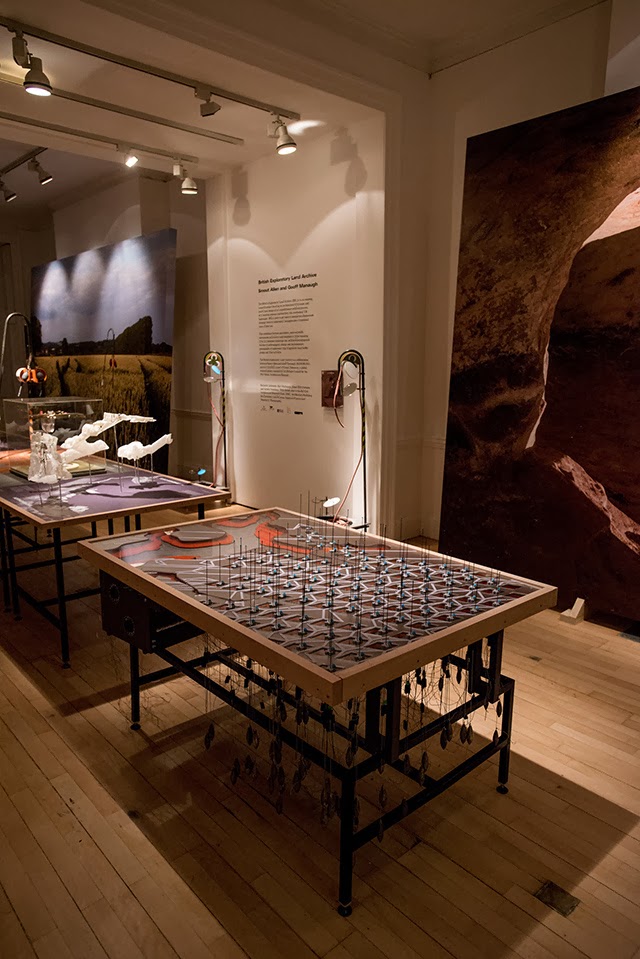
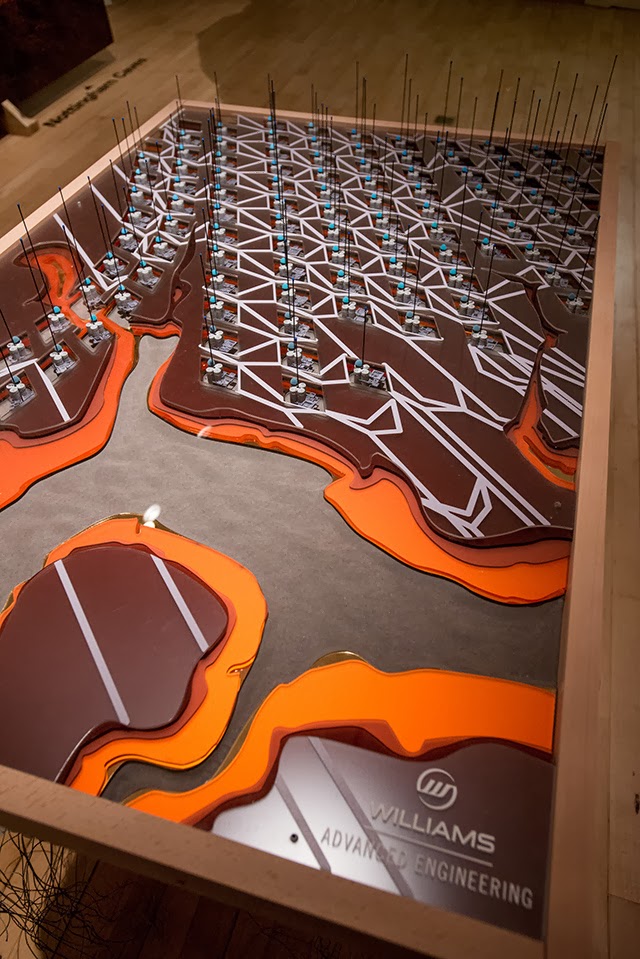
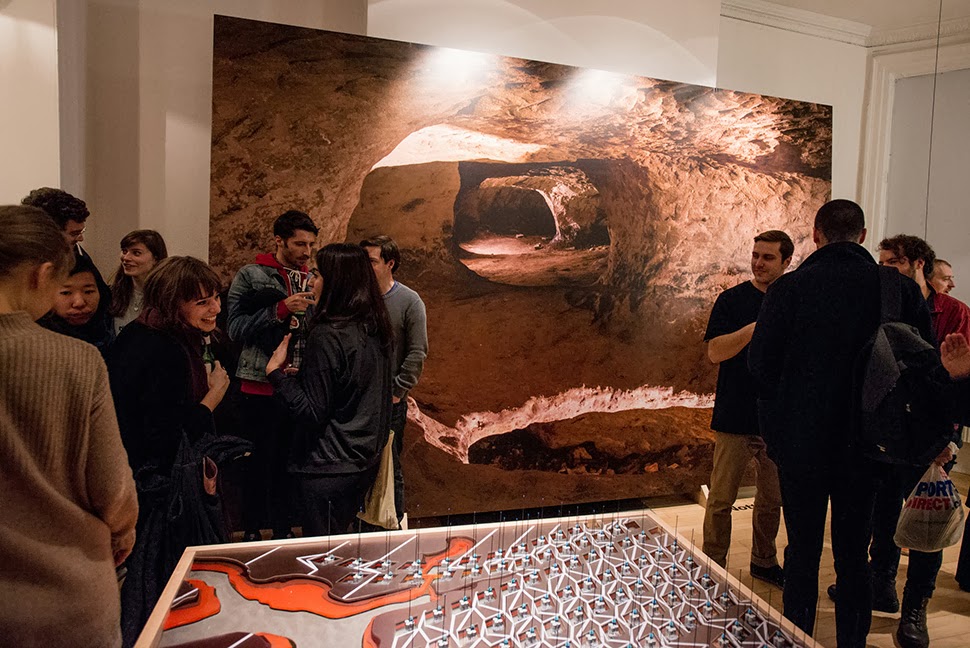
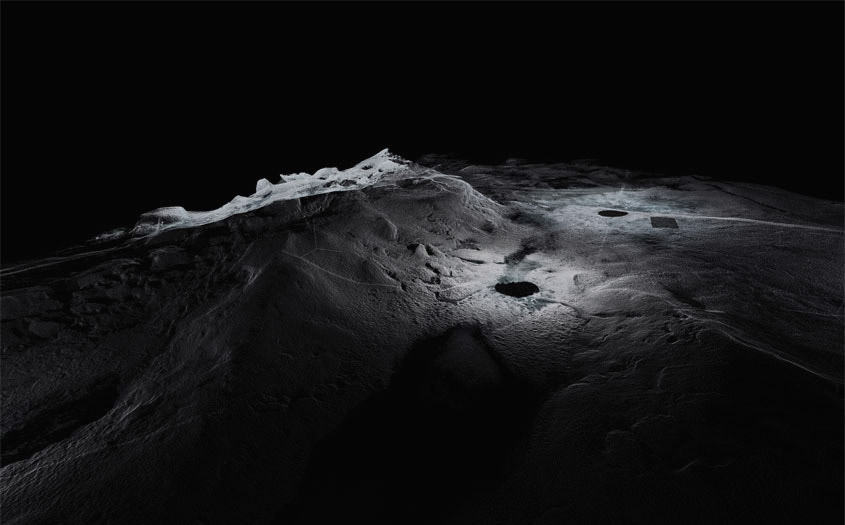
 The work on display ranged from cast models of underground sand mines in Nottingham, based on laser-scanning data donated by the
The work on display ranged from cast models of underground sand mines in Nottingham, based on laser-scanning data donated by the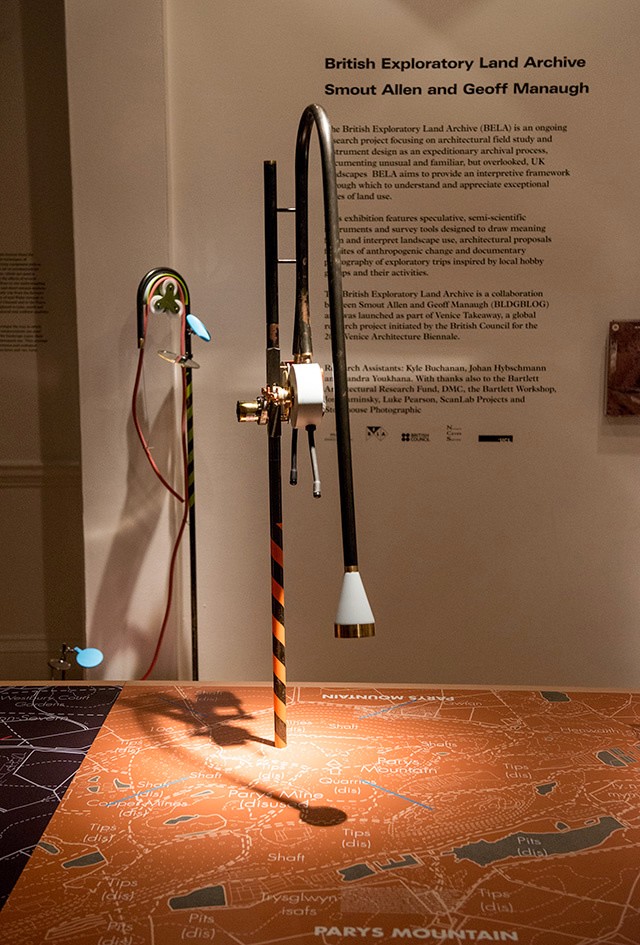  From the bizarre environmental-sensing instruments first seen back at the
From the bizarre environmental-sensing instruments first seen back at the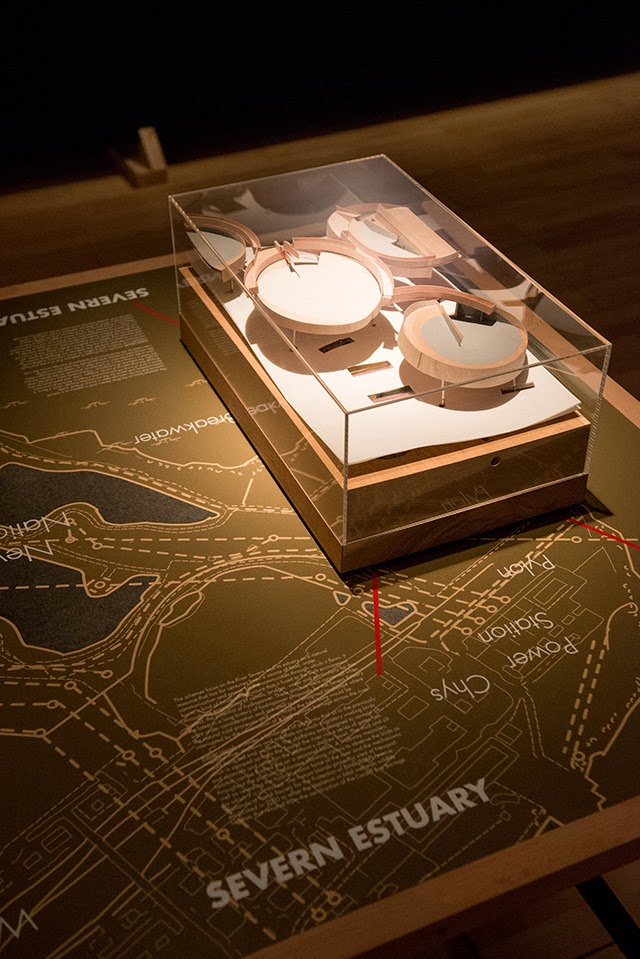 
 I should quickly add that the exhibition is, by far and away, the work of Smout Allen, who burned candles at every end to get this all put together; despite being involved with the project, and working with the ideas all along, since
I should quickly add that the exhibition is, by far and away, the work of Smout Allen, who burned candles at every end to get this all put together; despite being involved with the project, and working with the ideas all along, since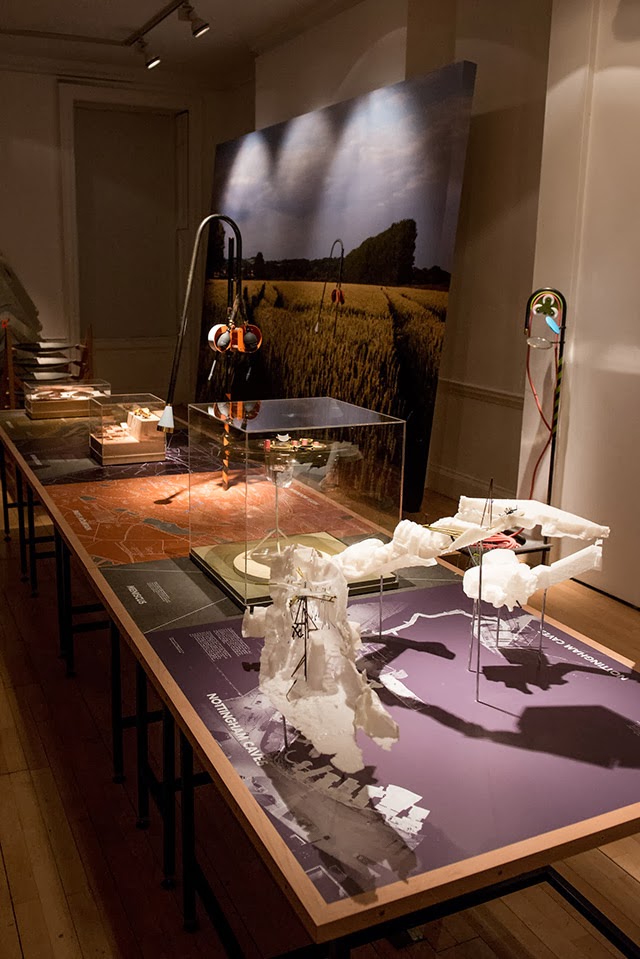  In any case, a brief note on the collaboration with
In any case, a brief note on the collaboration with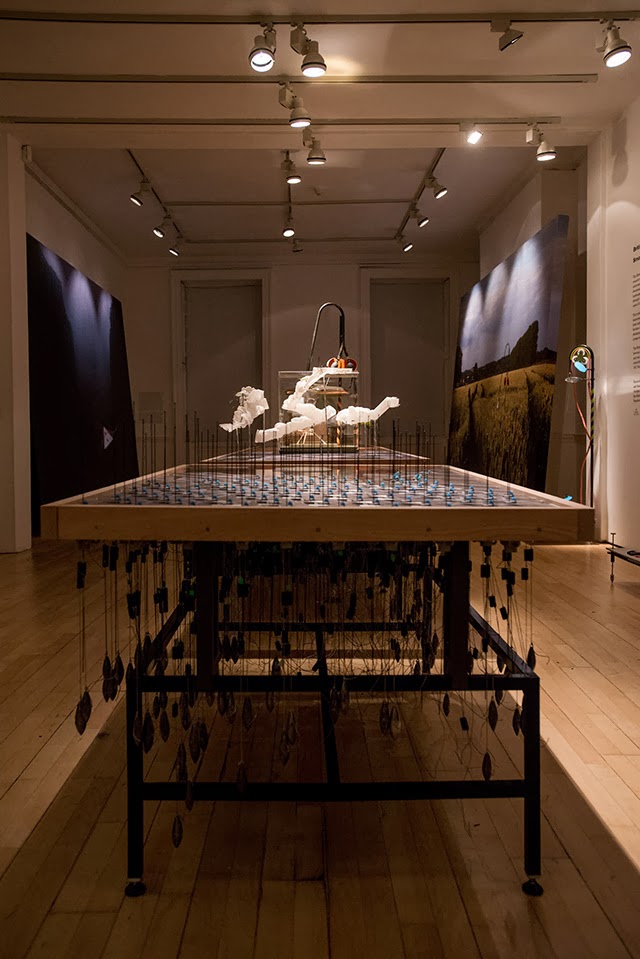  This would be an energy-storage landscape—in effect, a giant, island-sized, semi-subterranean field of batteries—where excess electrical power generated by the gargantuan offshore field of wind turbines called the
This would be an energy-storage landscape—in effect, a giant, island-sized, semi-subterranean field of batteries—where excess electrical power generated by the gargantuan offshore field of wind turbines called the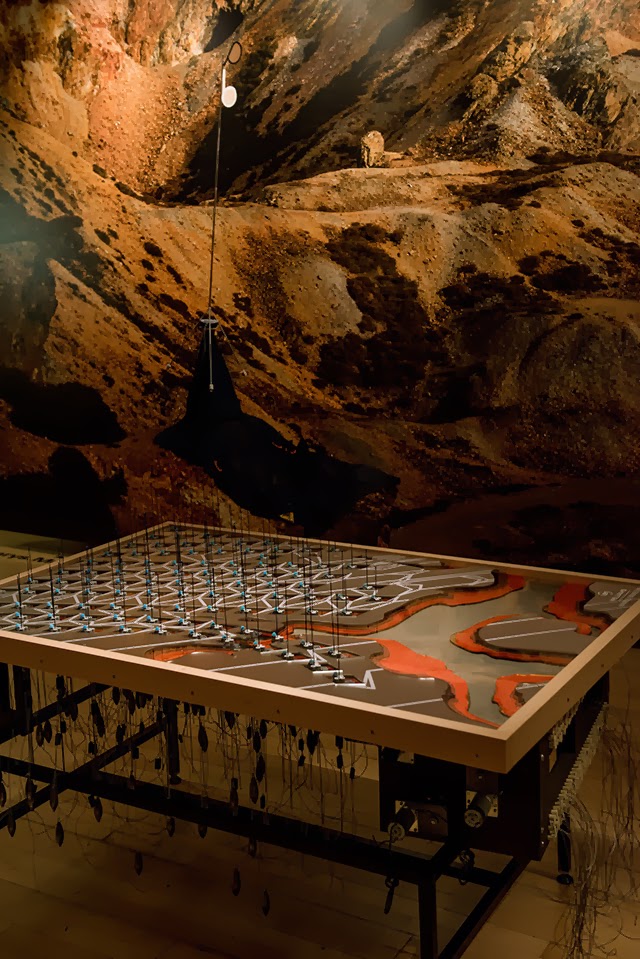 
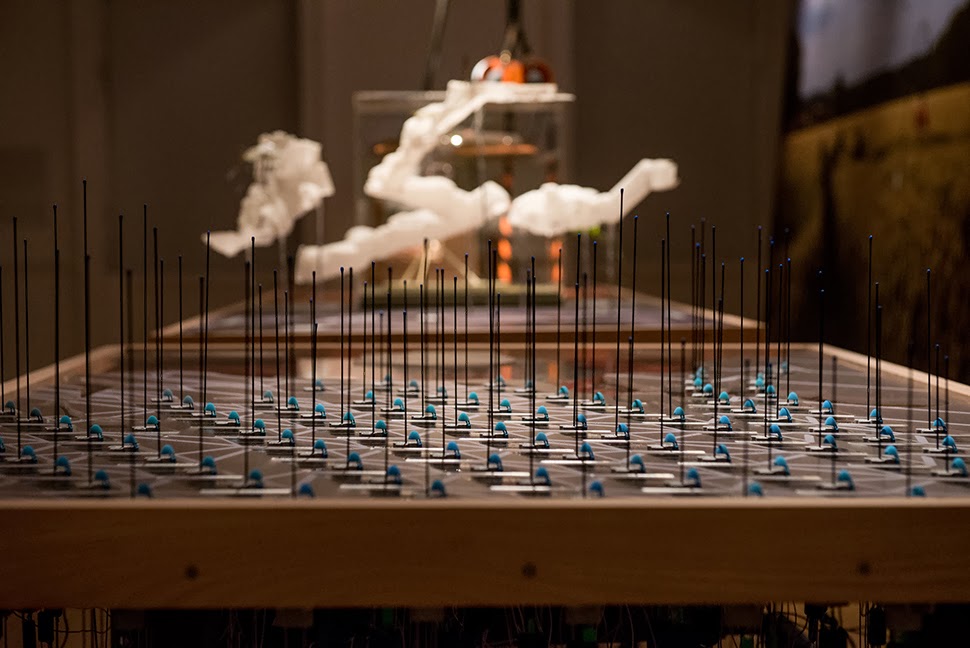
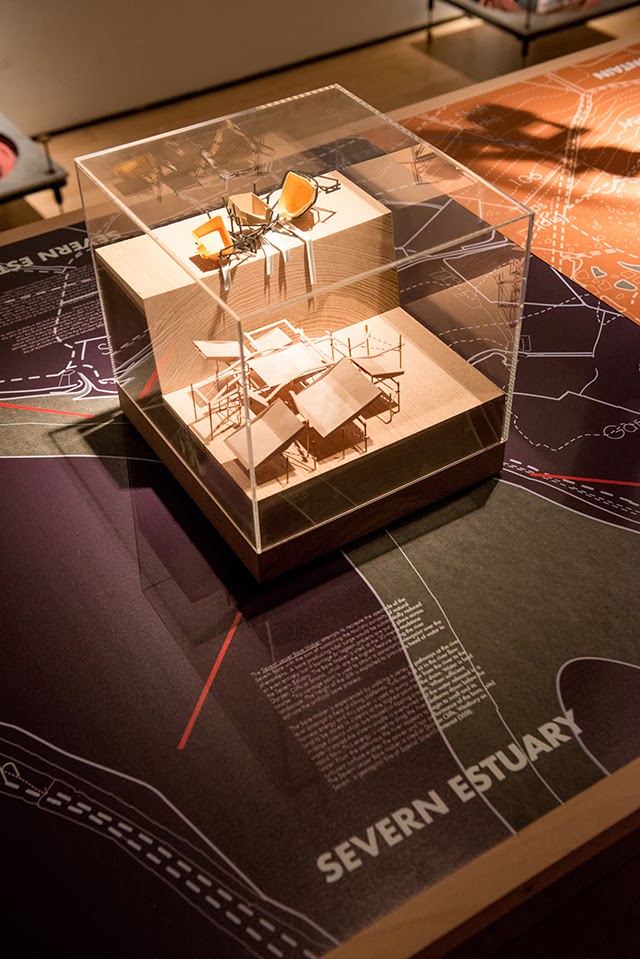
 This island of half-buried spinning machines included tiny motor parts and models based on Williams’ own
This island of half-buried spinning machines included tiny motor parts and models based on Williams’ own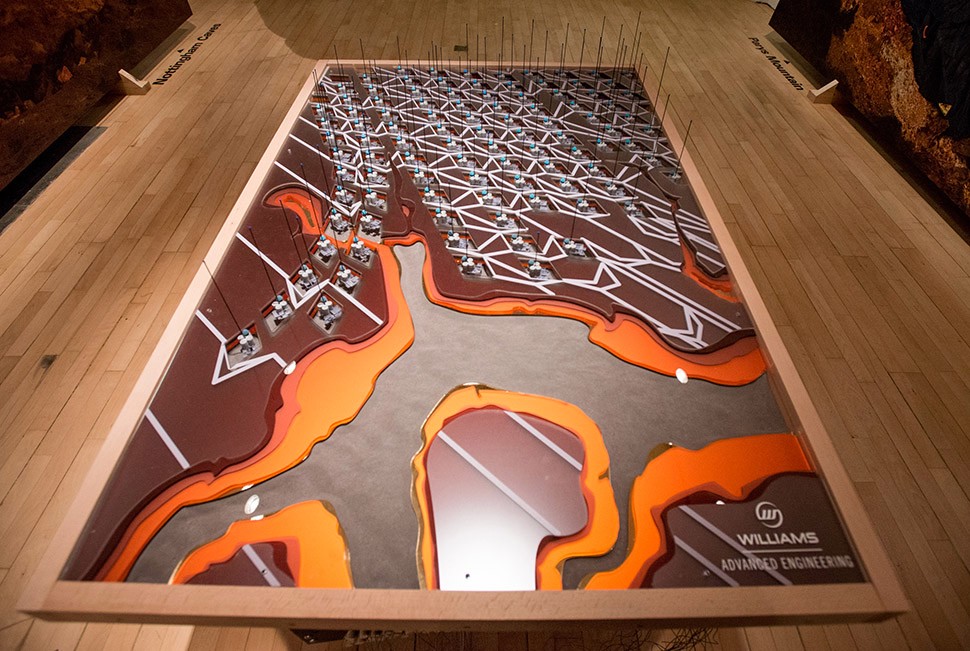 
 It was these little parts and models that were 3D-printed in alumide—a mix of nylon and aluminum dust—for us by engineers at Williams.
It was these little parts and models that were 3D-printed in alumide—a mix of nylon and aluminum dust—for us by engineers at Williams.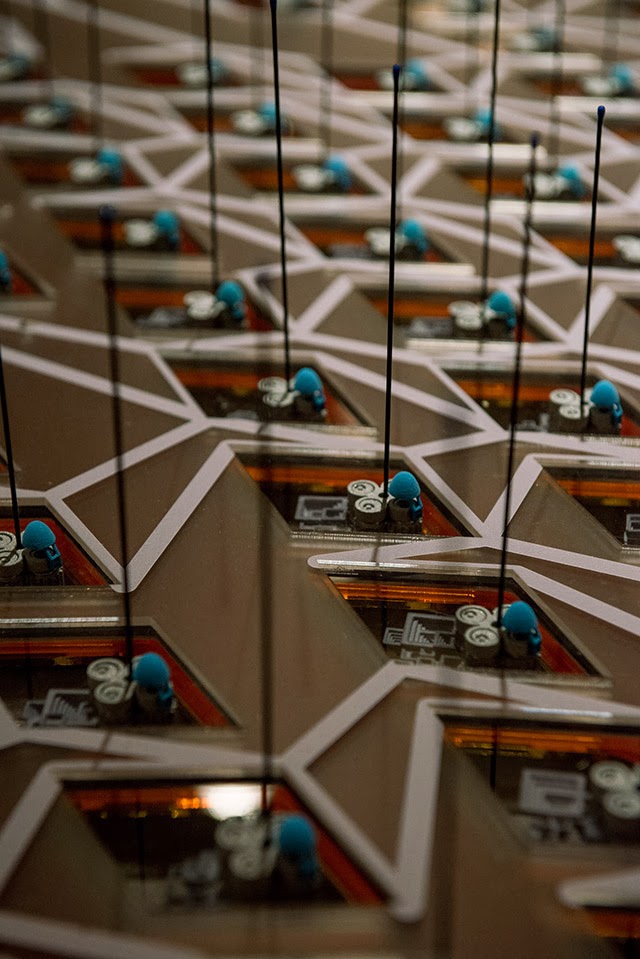  The very idea of a 3D-printed energy storage landscape on the British coast, disguised as an island, whirring inside with a garden of flywheels, makes my head spin, and a part of me would actually very much love to pursue feasibility studies to see if such a thing could potentially even be constructed someday: a back-up generator for the entire British electrical grid, saving up power from the
The very idea of a 3D-printed energy storage landscape on the British coast, disguised as an island, whirring inside with a garden of flywheels, makes my head spin, and a part of me would actually very much love to pursue feasibility studies to see if such a thing could potentially even be constructed someday: a back-up generator for the entire British electrical grid, saving up power from the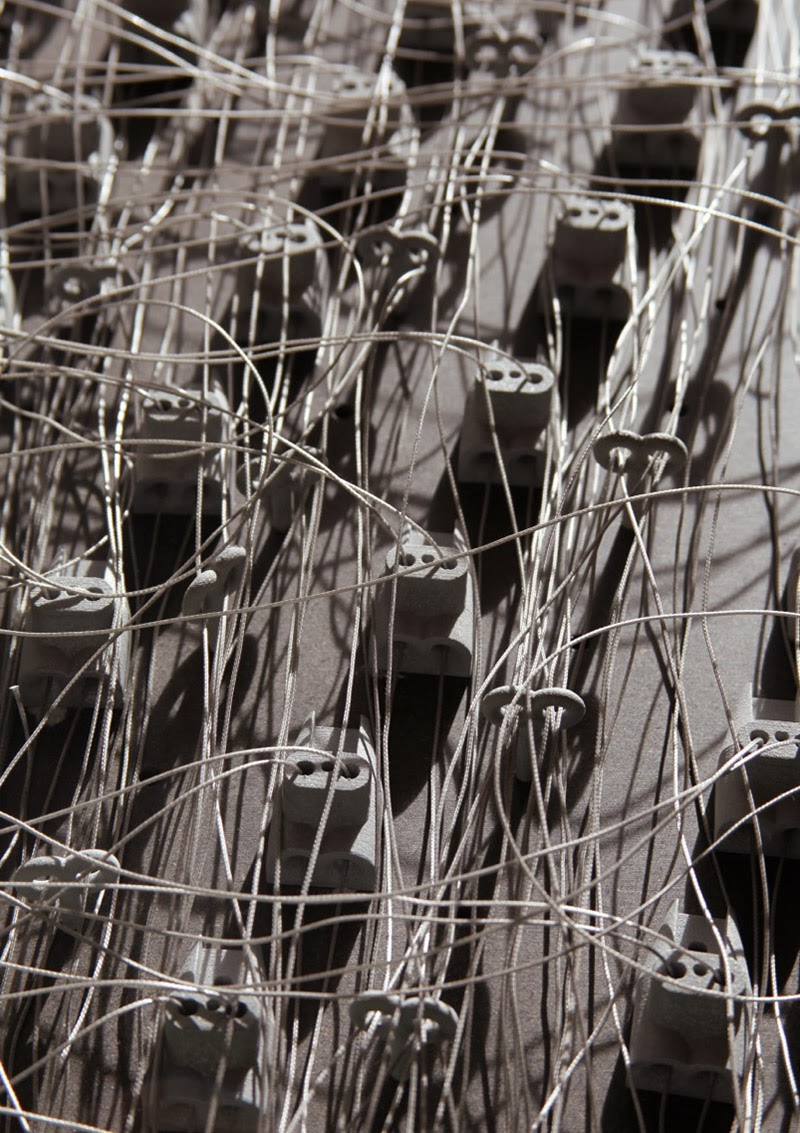  Finally, thanks not only to Williams, but to the
Finally, thanks not only to Williams, but to the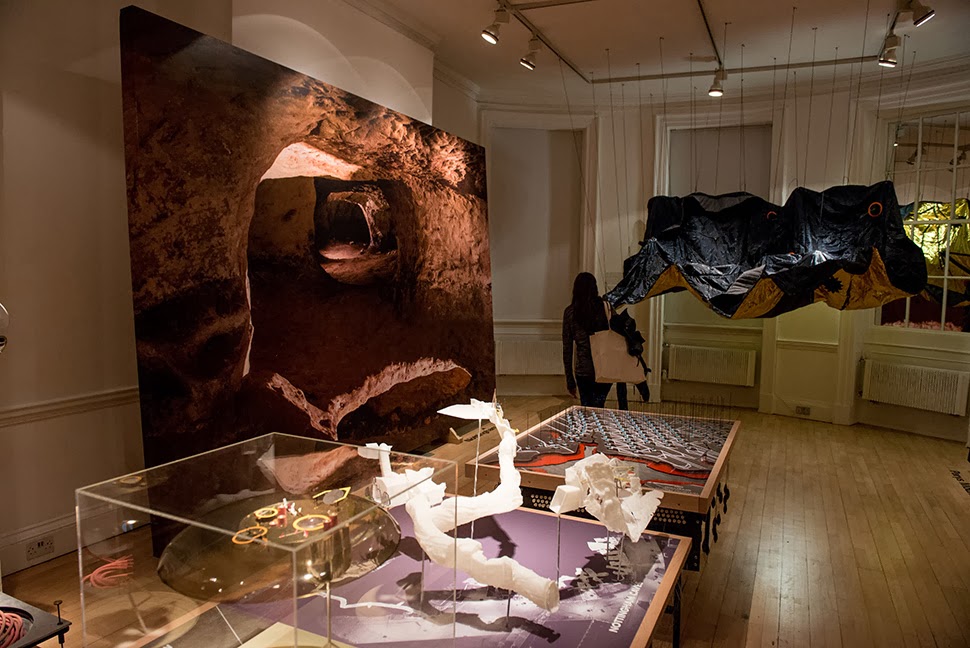 
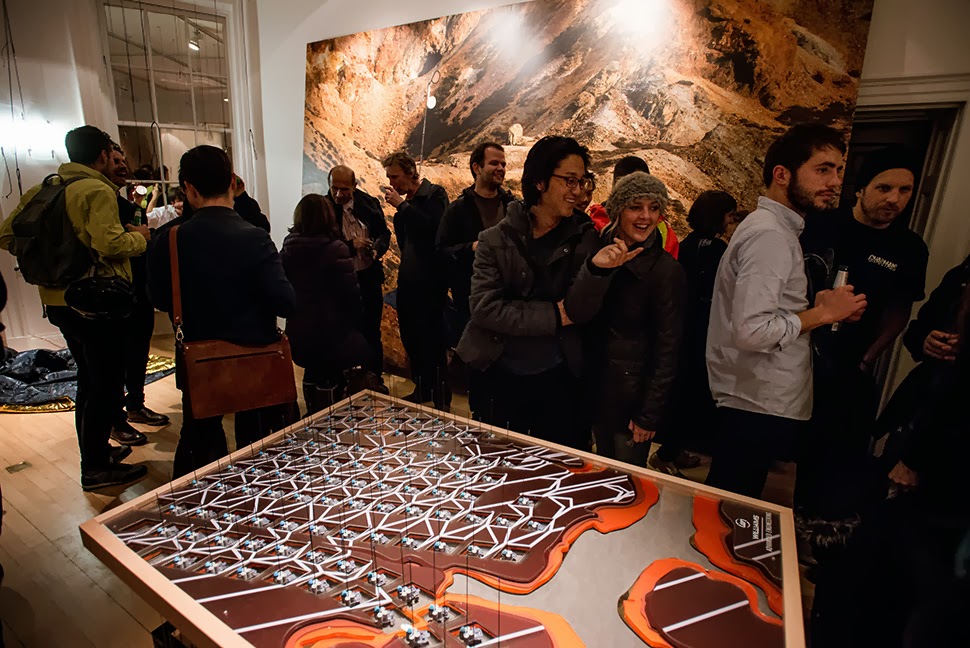
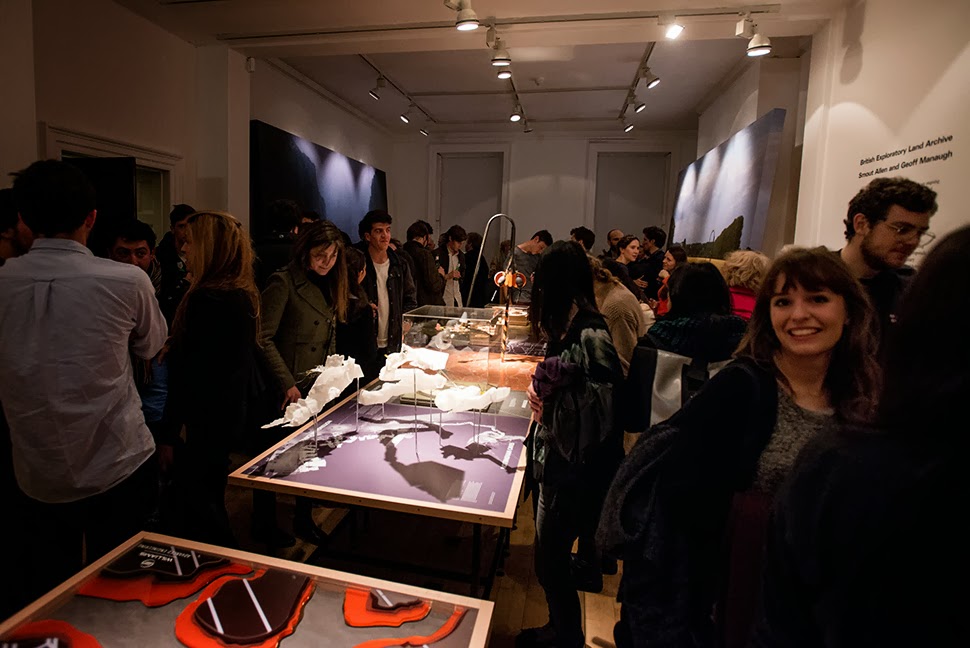
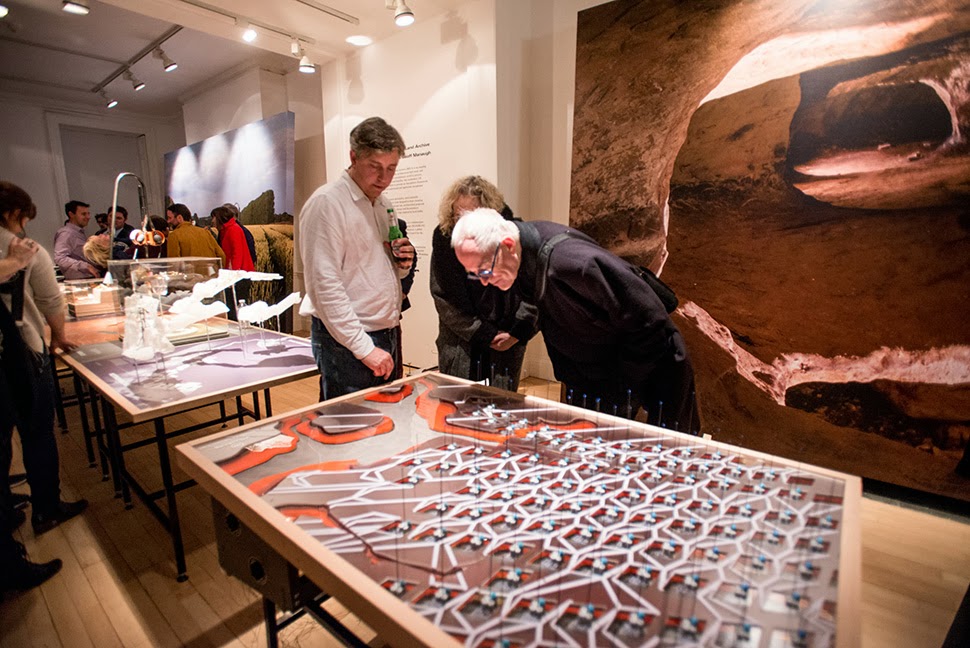




 The exhibition is
The exhibition is 
 [Image: A “
[Image: A “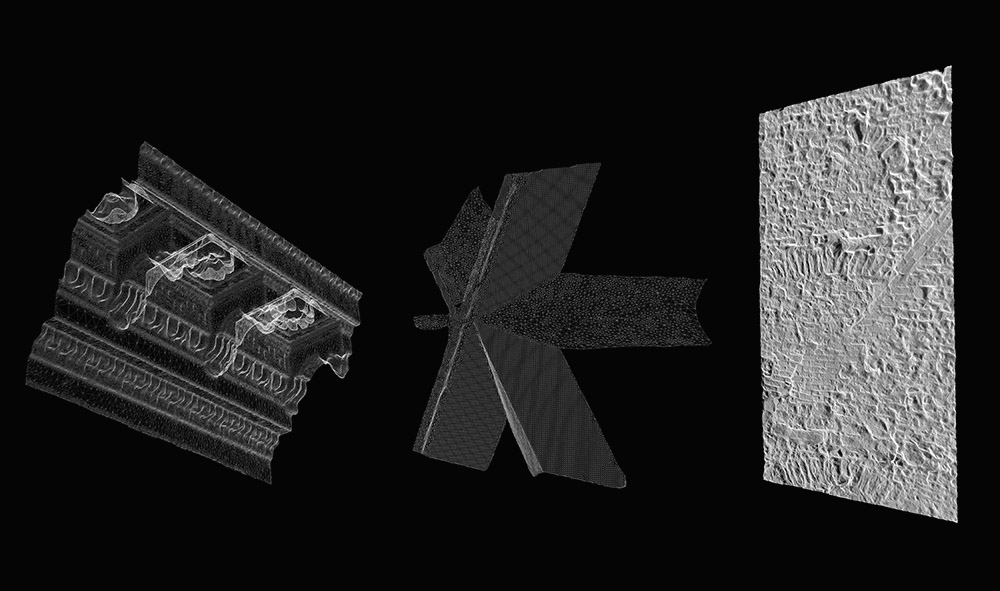 [Image: A “
[Image: A “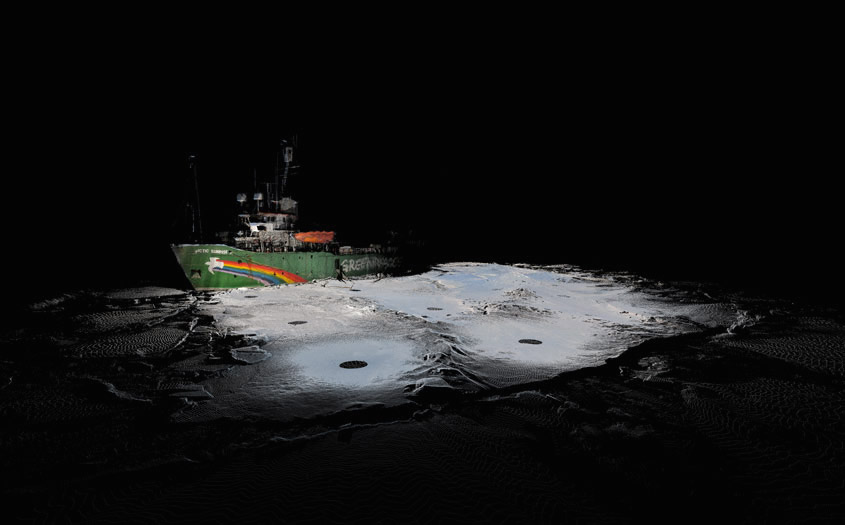
 [Images: From the “
[Images: From the “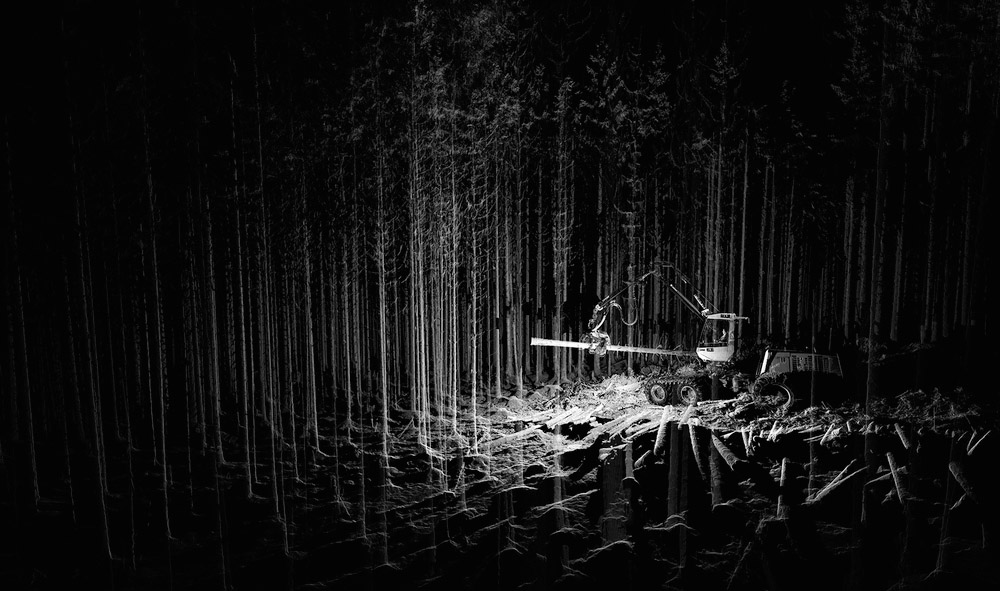 [Image:
[Image: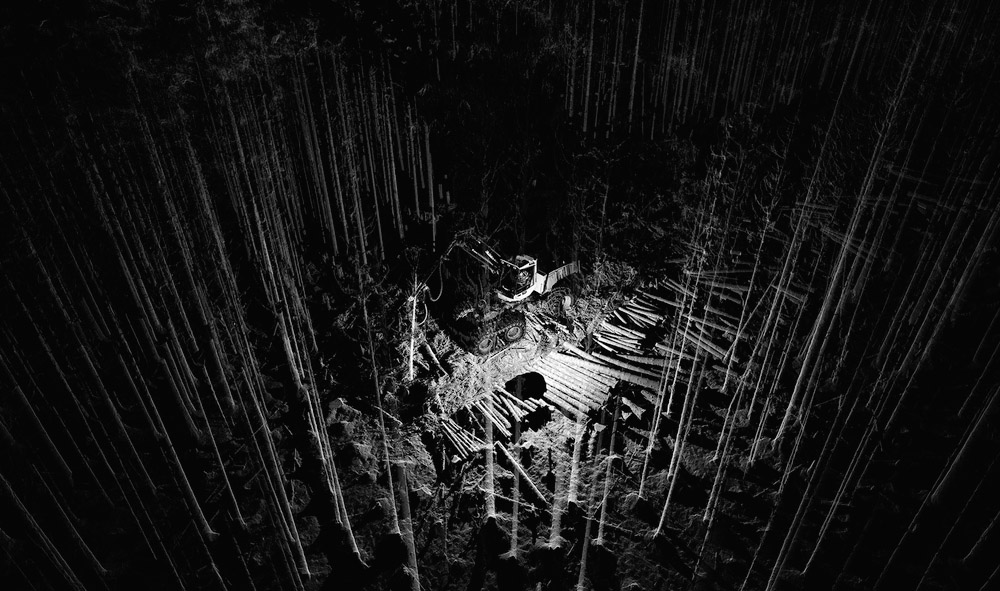 
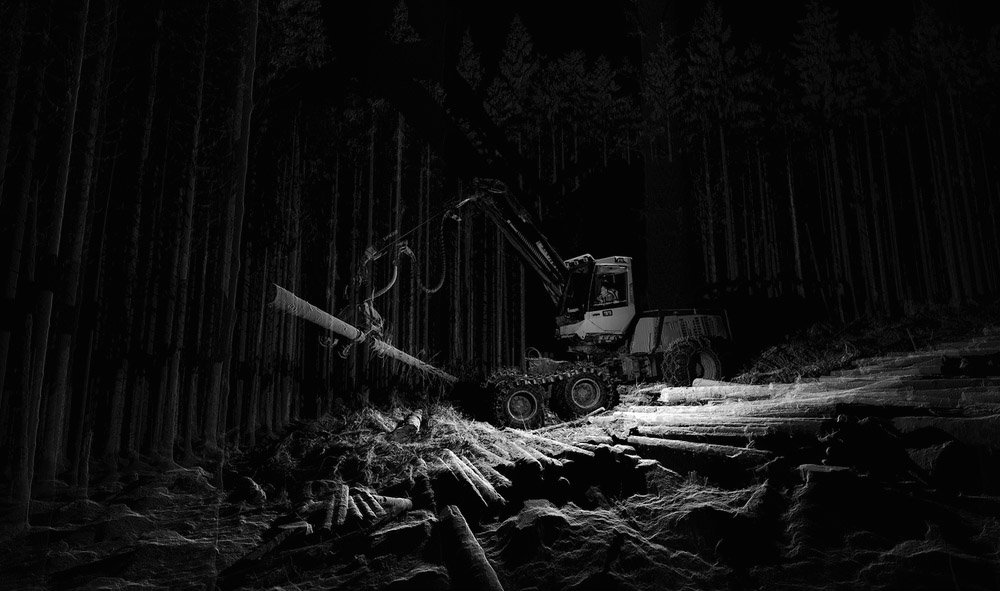
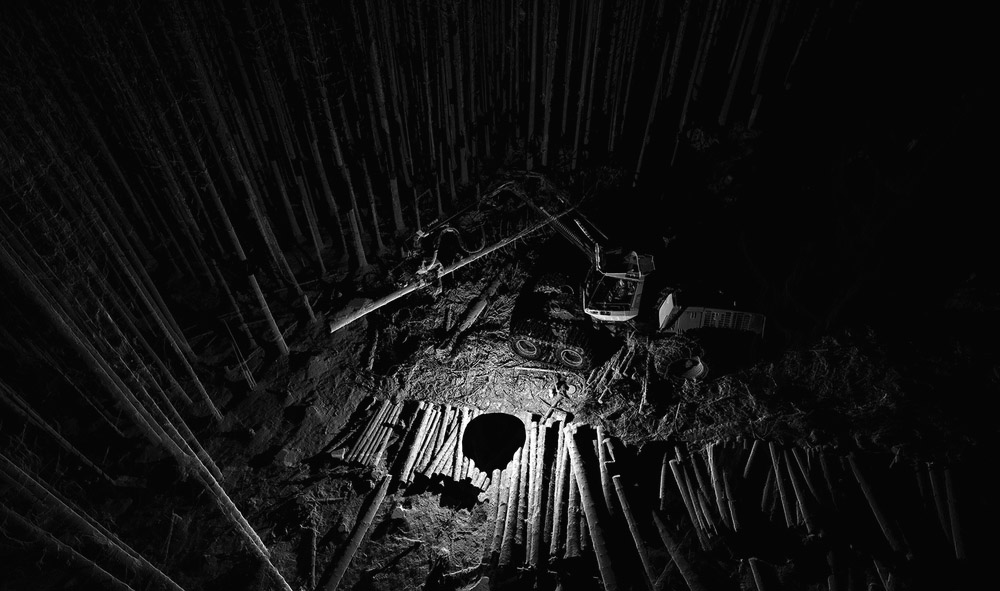
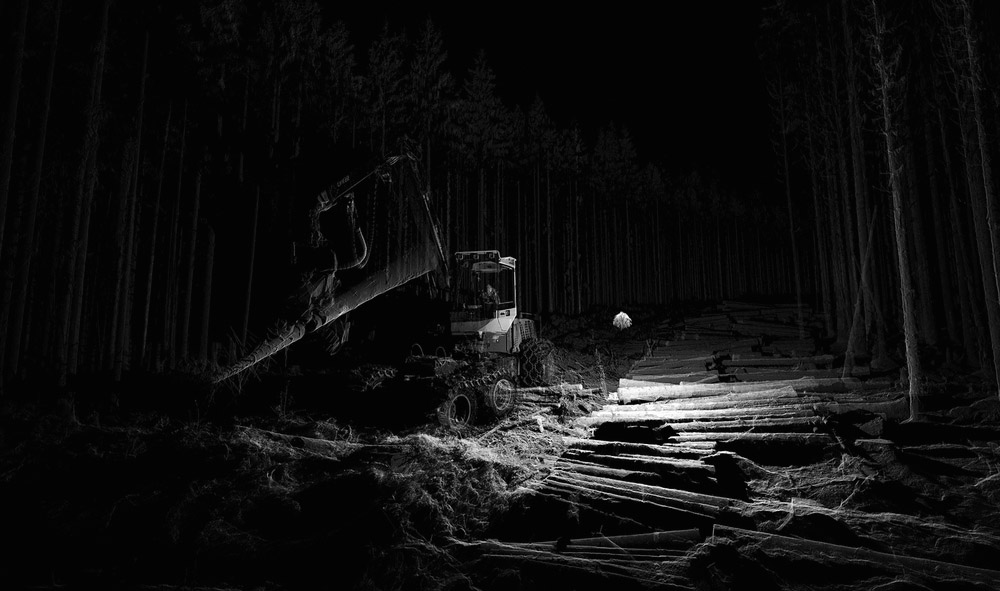

 [Image: Scans of a
[Image: Scans of a 
 The London-based architectural group
The London-based architectural group 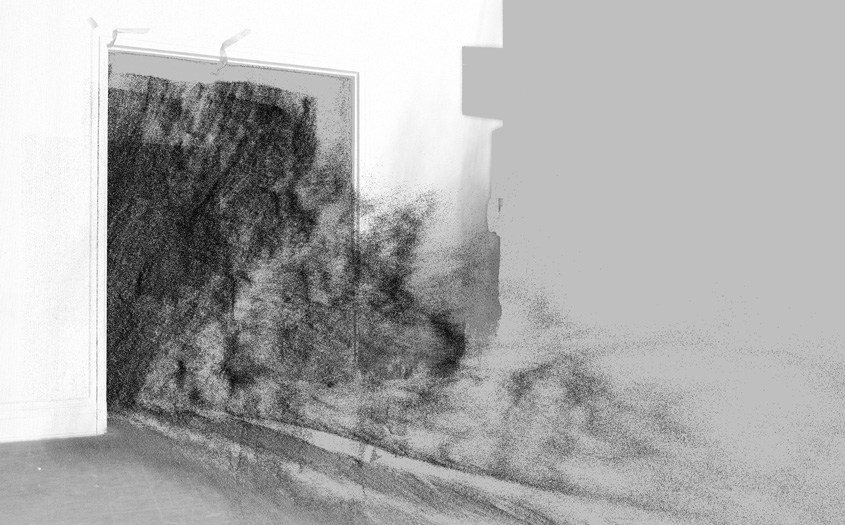 [Images: From
[Images: From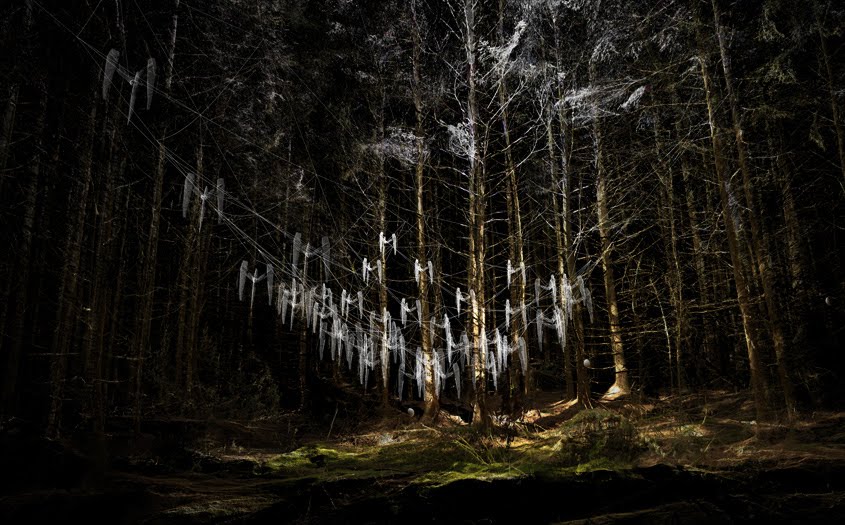  [Image: From
[Image: From  [Image: From
[Image: From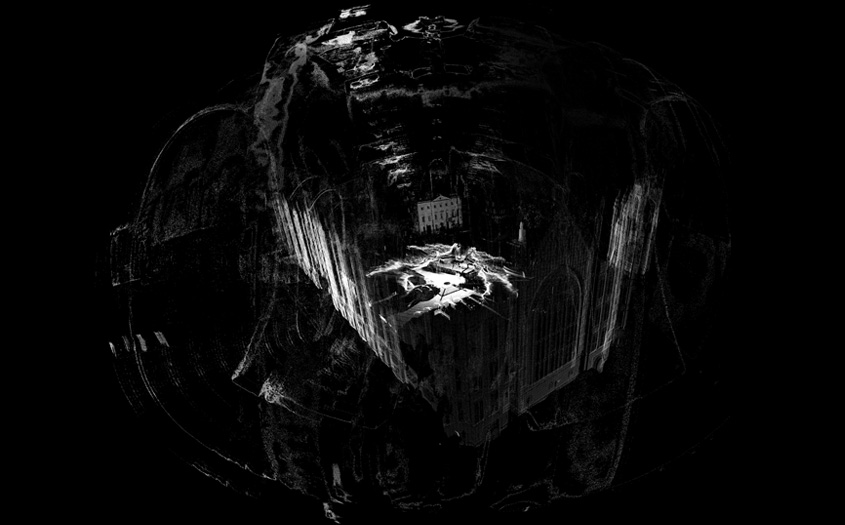 
 [Images: From
[Images: From 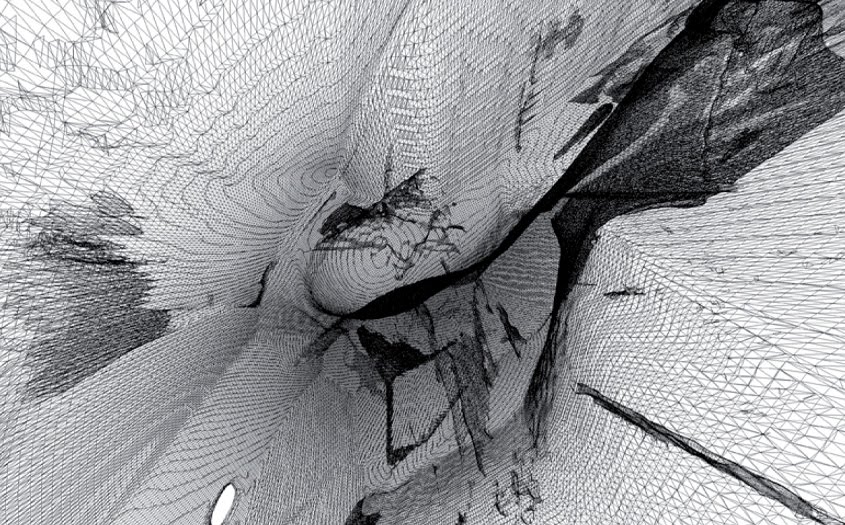 [Images: From
[Images: From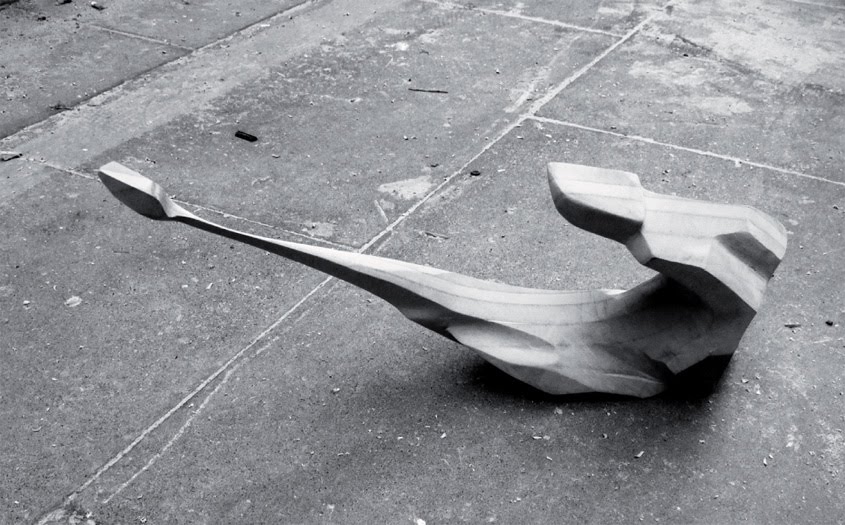 
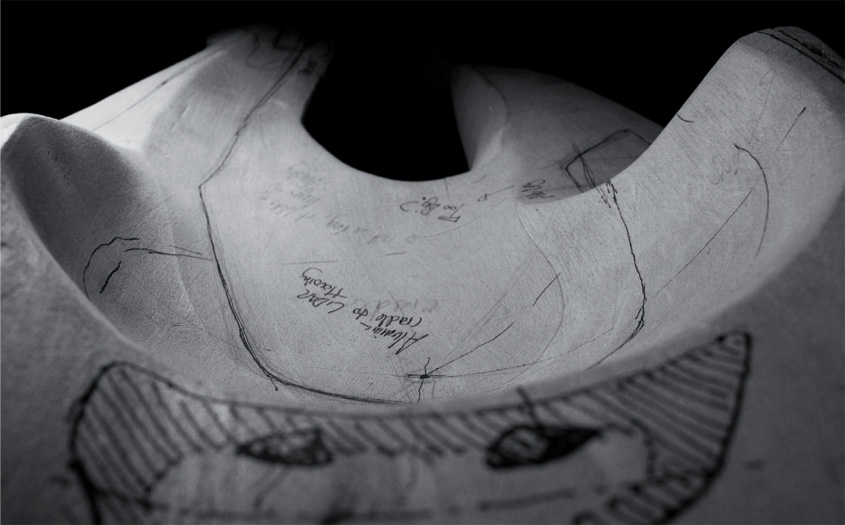 [Images: A hypothetical “stealth object,” resistant to laser-scanning, by ScanLAB].
[Images: A hypothetical “stealth object,” resistant to laser-scanning, by ScanLAB].